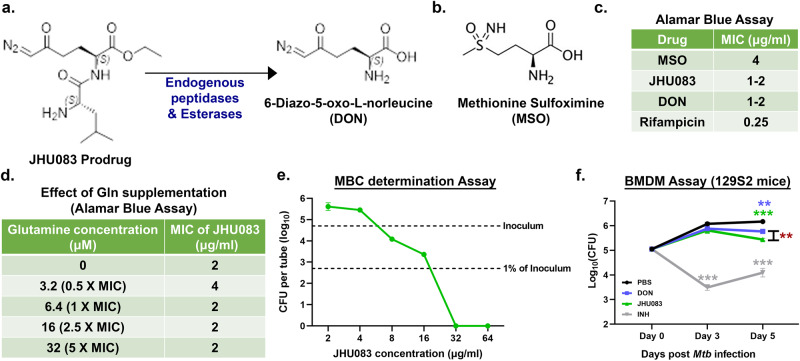
Fig. 1. JHU083 has direct antimycobacterial activity in vitro.
a Chemical structures of the prodrug JHU083 and the active drug DON. Endogenous host esterases and peptidases convert JHU083 into DON. b Chemical structure of MSO. c Table showing the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) values of the drugs against the Mtb H37Rv strain determined using the Alamar blue assay. d Table depicting the effect of glutamine (Gln) supplementation on the antimycobacterial activity of JHU083 using the Alamar blue assay. For each assay, a fixed concentration of Gln was used as shown with the assumed MIC of JHU083 being 2.0 μg/ml or 6.4 μM. e Graph showing the results of the minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) determination assay. The top dotted line represents the starting inoculum of the Mtb culture while the bottom dotted line represents 1% of the initial inoculum. f Antibacterial activity of drugs against Mtb growing within bone-marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs). IFNγ-activated BMDM from 129S2 mice were infected with Mtb H37Rv at an MOI of 2. They were then treated with 10 μg/ml of either DON or JHU083 (5x the MIC of each drug assuming the MIC is 2.0 μg/ml). Isoniazid (INH) at 1.28 μg/ml was used as the positive control. The cells were lysed at indicated time points and plated on 7H11 selection plates. The assay was performed as described in the “Methods”. Data were plotted as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed student t test considering unequal distribution. The exact p-values are provided in the Source Data file. * < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001. All the experiments were performed in triplicate.