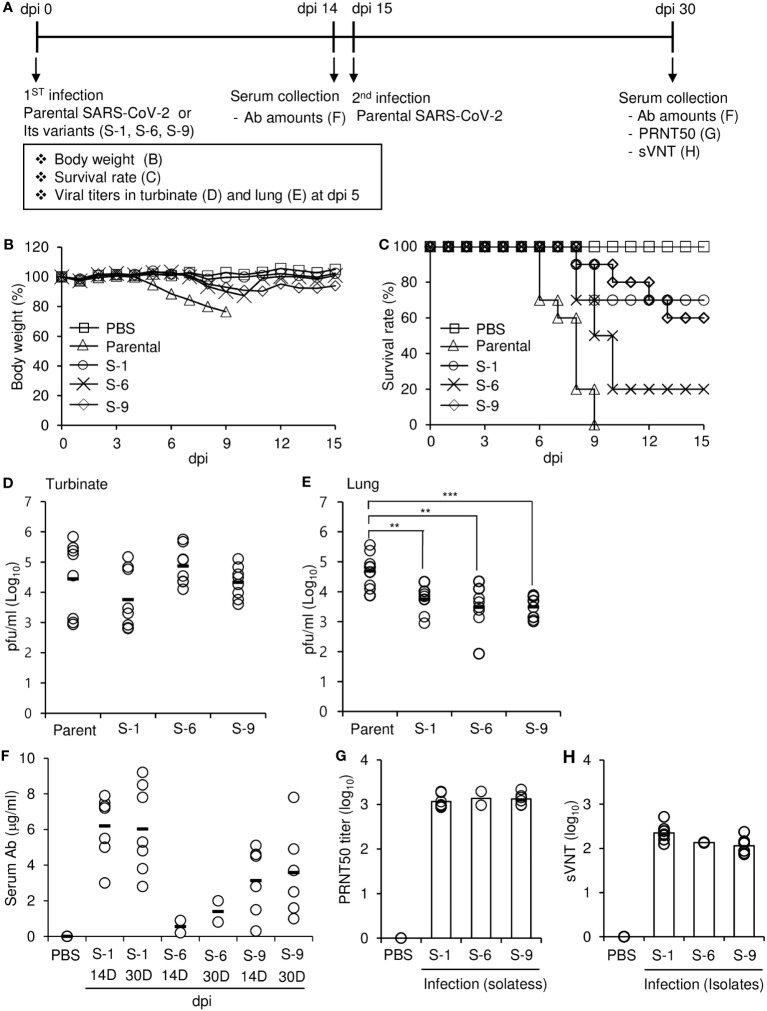
Figure 7.
Effects of parental SARS-CoV-2 and its variants on hACE2 transgenic mice (B6.Cg-Tg(K18-ACE2)2Prlmn/J). (A) Schematic diagram of the experiments. (B–E) Hemizygous K18-hACE2 mice were intranasally infected with 3 × 104 pfu/mouse of parental SARS-CoV-2 or its variants. Body weight (B) and survival (C) were measured for 15 days after intranasal infection (n = 10 per group). dpi, days post-infection. Turbinates (D) and lungs (E) were collected 5 days after intranasal infection (n = 8 per group). Viral loads in turbinate and lung homogenates were measured by plaque assay. The P values were determined by two-sided unpaired t-test. **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. (F–H) Hemizygous K18-hACE2 mice were intranasally infected with 3 × 104 pfu/mouse of parental SARS-CoV-2 or its variants (n = 10 per group). Serum was collected from surviving mice 14 days (14D) after infection. Fifteen days after the first infection, the surviving mice were intranasally challenged with 3 × 104 pfu/mouse of parental SARS-CoV-2. Serum was collected 15 days (30D) after the challenge. (F) The amounts of parental SARS-CoV-2 S protein RBD-specific IgG in the serum were determined by ELISA. (G) The PRNT50 of the serum collected at 15 days (30D) after the challenge was determined by plaque assay. (H) The sVNT of the serum collected at 15 days (30D) after the challenge was determined against parental SARS-CoV-2.