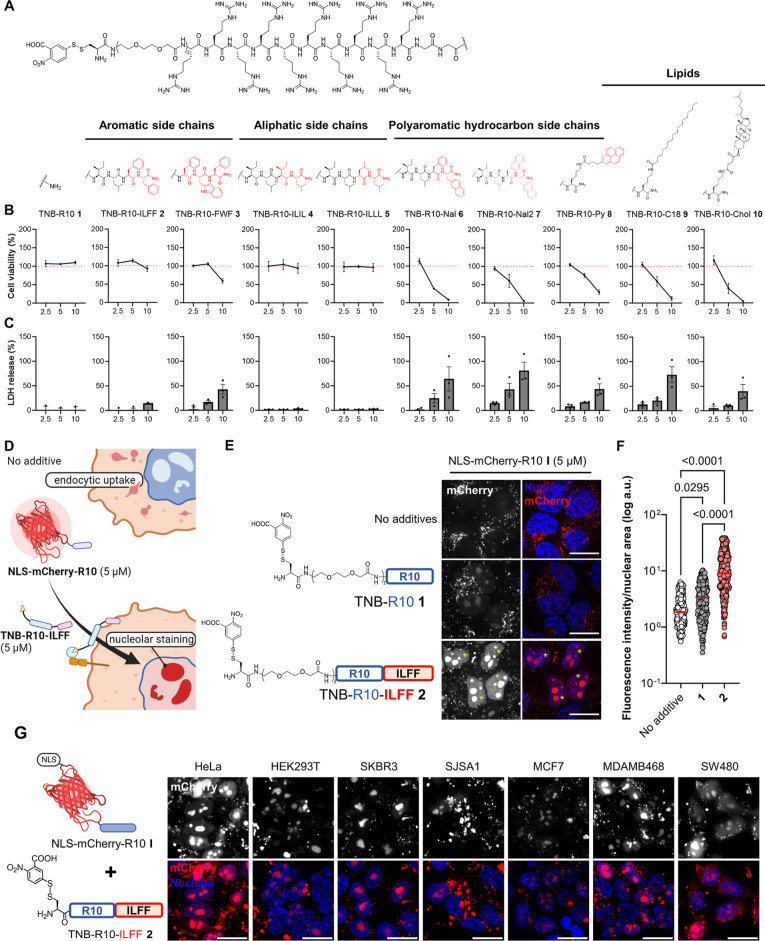
Figure 2.
Design and screening of CPP-additives with a hydrophobic motif. (A) Synthesized hydrophobic CPP-additives 1–10 with different hydrophobic motifs. (B) Cell viability as determined by WST-1 mitochondrial reduction assay after treating HeLa cells with 2.5, 5, or 10 μM hydrophobic CPP-additives 1–10 for 1 h in serum-free FluoroBrite DMEM. Red dotted line indicates 100% viability. (C) Analysis of membrane integrity following CPP-additive treatment as determined by measuring the release of LDH into the cell medium. Data presented as mean ± standard error (SE) of three biological replicates. (D) Rationale of the protein-CPP delivery assay. Without CPP-additives, NLS-mCherry-R10 I enters cells via endocytosis, while in the presence of CPP-additives, direct cytosolic uptake should occur and the NLS-mCherry-R10 I accumulates on the nucleolus. (E) Confocal microscopy images of cells treated with NLS-mCherry-R10 I in the presence or absence of indicated CPP-additives (5 μM) for 1 h in serum-free FluoroBrite DMEM. (F) Individual nuclear fluorescence intensities of 300 cells across three biological replicates following cotreatment with NLS-mCherry-R10 and CPP-additive. Red bar corresponds to the median fluorescence intensity of each treatment. P-values were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. (G) Nucleolar staining in different cell lines treated with I (5 μM) and 2 (5 μM) for 1 h in serum-free FluoroBrite DMEM. Scale bars: 20 μm.