Fig. 5.
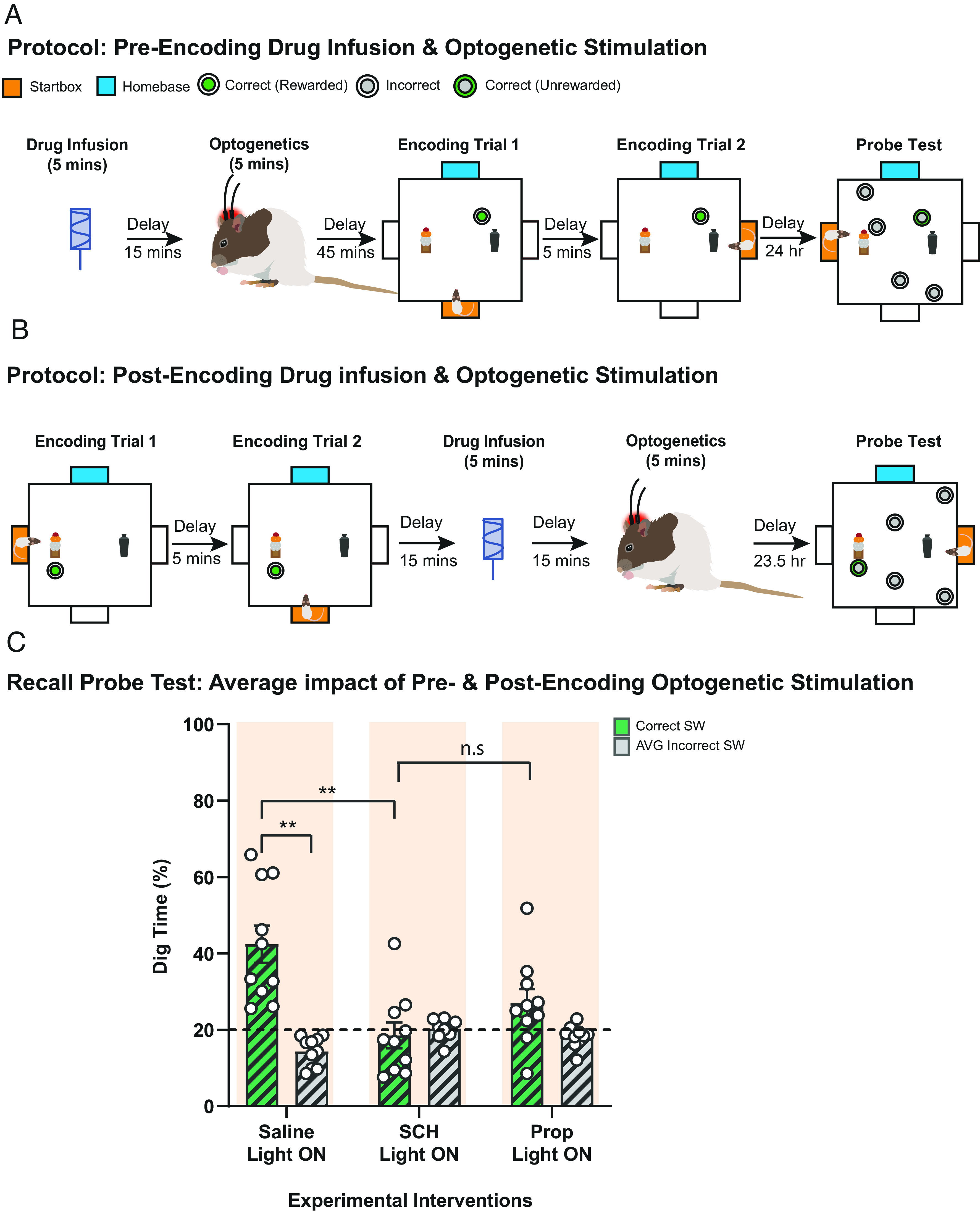
Pharmacological interventions in HPC and optogenetic stimulation of LC-TH+ neurons. (A and B) Experimental design for the pharmacological interventions and optogenetic preencoding (A) and postencoding (B) stimulation. Specific intrahippocampal drug infusions were administered 15 min prior to LC-TH+ stimulation, scheduled either before (A) or after (B) memory encoding during STs. (C) Blockade of hippocampal dopamine D1/D5 receptors (SCH) during LC-TH+ optogenetic stimulation abolished memory retention at 24-h PT. The effect of blockade of hippocampal β-adrenoceptor (Prop) was at an intermediate level, not significant than that for the control saline condition (n.s.). Means ± SEM and individual animal data plots. Dashed line in panel C indicates chance level. ns, not significant. **P < 0.01.
