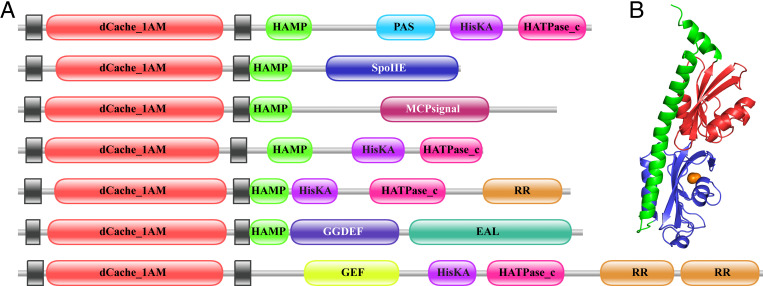
Fig. 1.
(A) Representative domain architectures of dCache_1AM proteins. A schematic representation of several protein architectures that contain dCache_1AM domains. Transmembrane helices are present at both ends of dCache_1AM (black boxes). The remaining domains are an α-helical domain, HAMP; a sensor domain, PAS; a dimerization, and phospho-acceptor domain of histidine kinases, HisKA; a C-terminal ATPase domain, HATPase_c; a serine/threonine phosphatase, SpoIIE; a methyl-accepting chemotaxis domain, MCPsignal; a response regulator receiver domain, RR; a diguanylate cyclase, GGDEF; a diguanylate phosphodiesterase, EAL; a cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) receptor, GAF. From top to bottom, protein architectures in this figure correspond to the following accession numbers from the non-redundant protein database: WP_011034866.1, WP_027185430.1, WP_014528895.1, WP_091710416.1, WP_015707342.1, WP_056043800.1, WP_052635864.1. (B) A typical structure of the dCache_1 domain. The figure shows protein database (PDB) structure ID 3LIB (10). The two Cache domains are colored blue and red, while the ligand position in the proximal Cache domain is shown as an orange ball.