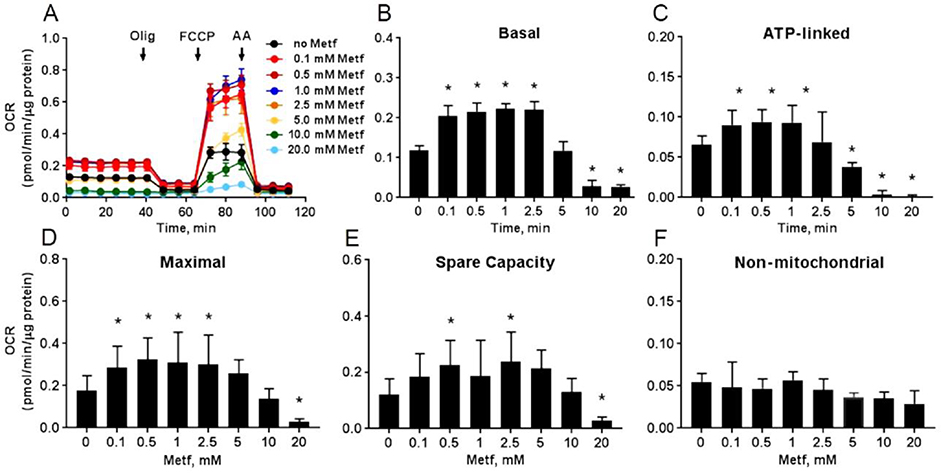
Fig. 1. Metformin dose-dependently alters respiration of cardiomyocytes.
(A) Raw traces of hiPSC-CMs oxygen consumption rate (OCR) recorded by XF96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer. The cardiomyocytes were exposed to different concentrations of metformin (Metf, 0 – 20 mM) for 24 h before the experiment. A basal measurement was recorded in the unbuffered DMEM supplemented with 11 mM glucose, followed by addition of 10 μM oligomycin A (Olig), 2 μM carbonyl cyanide p-triflouromethoxyphenylhydrazone (FCCP), and 10 μM antimycin A (AA). Treatment with Metf of ≤ 2.5 mM increased and ≥ 5 mM inhibited (B) basal, (C) ATP-linked, (D) maximal, (E) spare capacity OCR. There was no change in non-mitochondrial OCR (E) in the cardiomyocytes. Data are presented as mean ± SD; * p < 0.05 compared to no Metf (t-test for normally distributed variables and Kruskal-Wallis test for the variables that were not following the normal distribution); n=3.