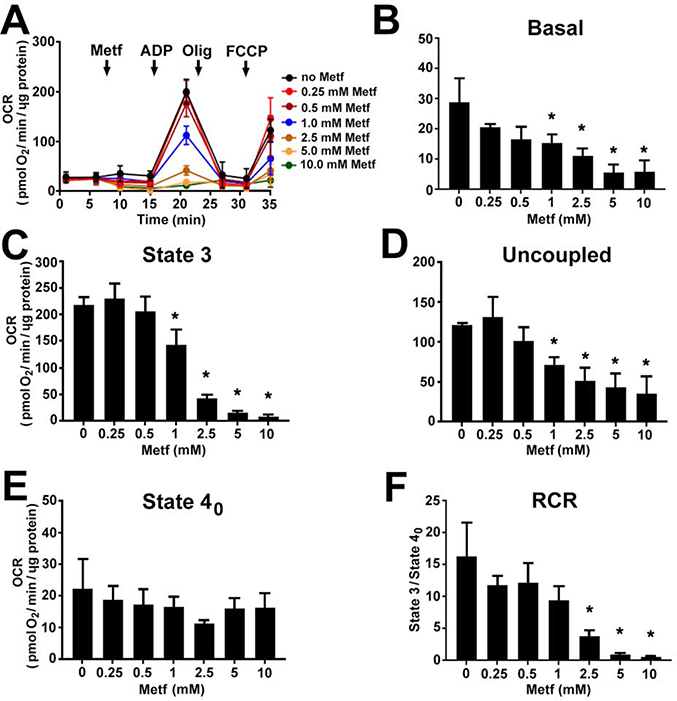
Fig. 4. Metformin dose-dependently decreases complex I-mediated respiration in isolated cardiac mitochondria.
(A) Traces of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) recorded by XF96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer in isolated mitochondria oxidizing 5 mM glutamate and 2 mM malate after addition of metformin (Metf, 0.25 – 10 mM), followed by injection of 4 mM ADP (State 3), 2.5 μg/ml oligomycin A (Olig, State 4o), and 3 μM FCCP (Uncoupled). Metformin dose-dependently reduced (B) basal, (C) state 3, (D) uncoupled OCR, and respiratory control ratio (RCR, State 3/State 4o). Metformin exposure did not change (E) state 4o OCR. Data are expressed as mean ± SD; * p < 0.05 compared to no Metf (t-test for normally distributed variables and Kruskal-Wallis test for the variables that were not following the normal distribution); n=3.