Figure 1. Prior chronic ingestion of subtoxic doses of Cd enhances IgE responses and allergy severity.
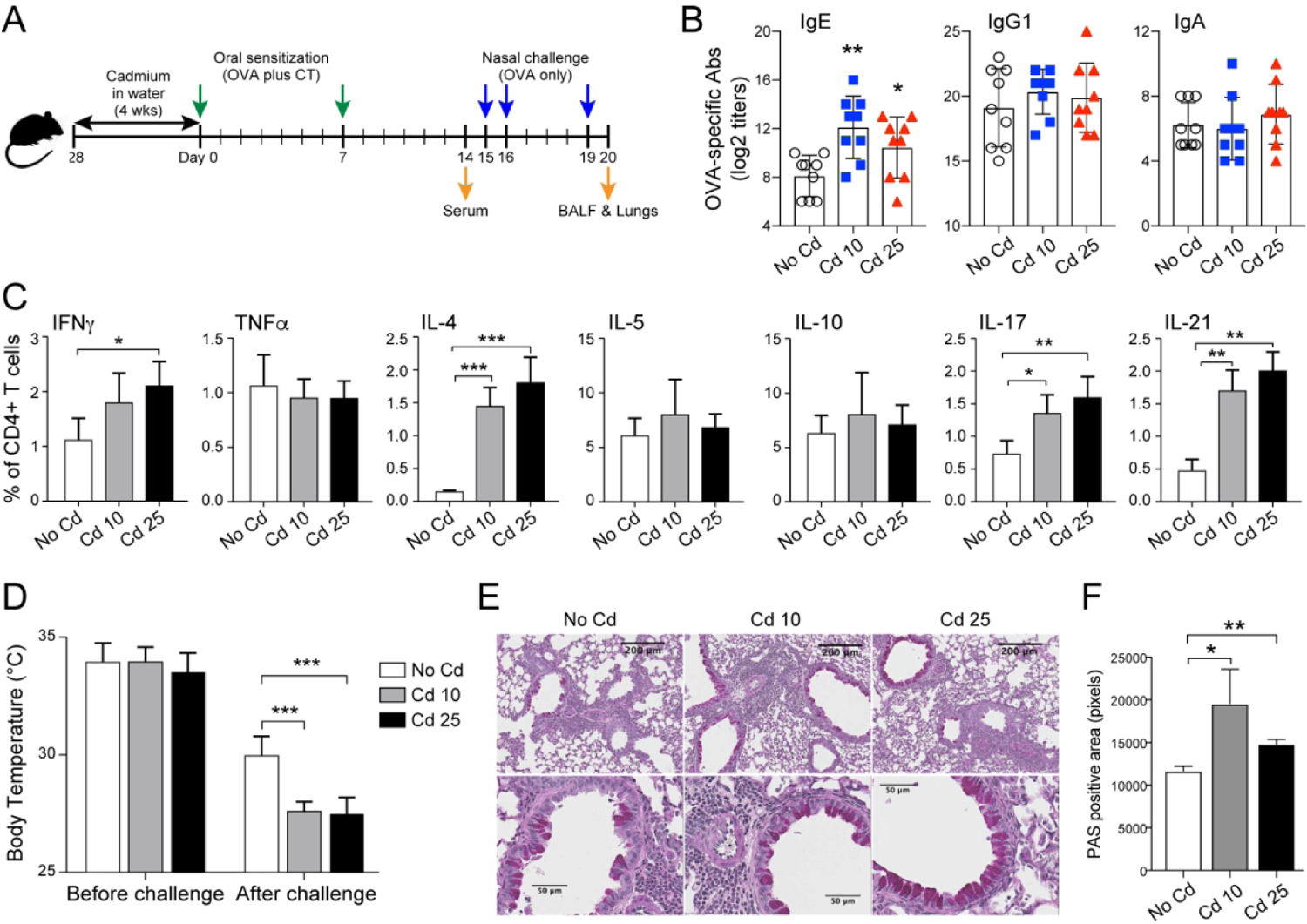
(A) Experimental scheme. Mice (n=5 per group) were provided CdCl2 [10 μM (Cd10) or 25 μM (Cd25)] in drinking water for 28 days and sensitized by the oral administration of OVA (1 mg) and cholera toxin (CT 15 μg). (B) OVA-specific serum Ab titers 1 week after the last sensitization (Day 14). (C) Allergen-specific CD4+ T cell responses. Spleens were collected on day 14 and restimulated in vitro with 1 mg/mL of OVA before flow cytometry analysis of CD4+ T cell cytokine responses. (D) Surface body temperatures of anesthetized mice before and 1 h after nasal allergen challenge with OVA (200 μg). (E) Lung inflammation and mucus production, and (F) quantification of mucus production. Data represent one of at least four independent experiments with five mice per group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 compared to No Cd.
