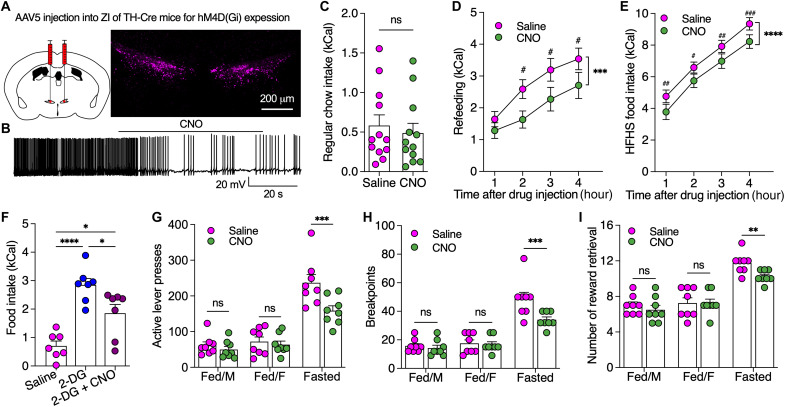
Fig. 3. Chemogenetic inhibition of ZI DA neurons decreased motivated food seeking and consumption.
(A) AAV was injected to bilateral ZI of TH-Cre mice to express inhibitory hM4D(Gi) in ZI DA neurons. (B) A representative trace shows that CNO (3.0 μM) inhibited a ZITH-hM4D(Gi) neuron. (C) Regular food intake of fed mice (n = 12) over 4 hours following saline and CNO injection. (D) Refeeding after 24 hours fasting following saline and CNO injection. (E) HFHS food intake following saline and CNO injection. (F) Food intake over 4 hours following injection of saline, 2-DG (200 mg/kg), or 2-DG plus CNO (2.0 mg/kg). n = 7 each group. (G to I) Bar graphs showing active lever presses, breakpoints, and number of rewards earned in both fed and fasted mice (70% of their daily food intake overnight) during operant PR tests of 45 min following saline or CNO (2.0 mg/kg) injection. Paired t test for (C), two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test [(D), (E), and (G) to (I)], one-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test (F).