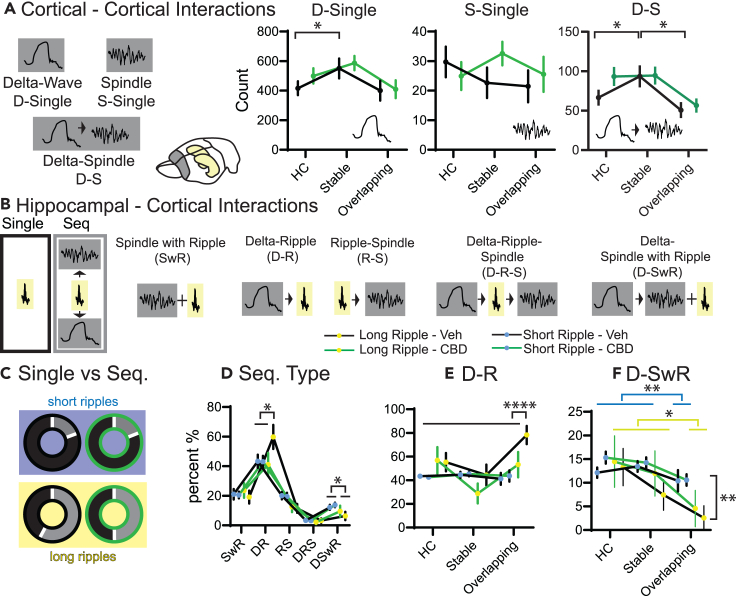
Figure 4.
Oscillation interactions
(A) Cortical interactions. Oscillations can be single delta (D) or spindle (S) waves, or coupled delta-spindle events (D-S). Counts of events shown for three different conditions home cage (HC), Stable and Overlapping (each rmANOVA with condition and treatment, D-single condition F2,62 = 3.9 p = 0.026 other p > 0.2, S-Single all p > 0.13, D-S condition F2,62 = 6.2 p = 0.0034, treatment F2,62 = 3.4 p = 0.076, interaction p = 0.29, orthogonal comparison run only for condition collapsing treatment).
(B) shows different types of oscillatory coupling.
(C) Fraction of short (top blue background) and long (bottom yellow background) that are part of sequences (gray) or occur alone (black). Left vehicle (black edge), right CBD (green edge). There was a significant effect (chi-square 534.2 p < 0.0001).
(D) Fraction of coupled long and short ripples spread over the different interaction types (sequence types F4,160 = 77 p < 0.0001, sequence types X ripple types F4,160 = 2.3 p = 0.06, other p > 0.16).
(E) As in D fraction of events that are D-R but split for the different conditions (condition F2,204 = 5.2 p = 0.006, ripple type F1,204 = 7.2 p = 0.0081, treatment F1,204 = 3.1 p = 0.08, condition X ripple type F2,204 = 7.4 p = 0.008, ripple type X treatment F1,204 = 3.9 p = 0.05, other p > 0.2).
(F) Same for D-SwR (condition F2,204 = 6.5 p = 0.0018, ripple type F1,204 = 5.5 p = 0.019 other p > 0.18). Only in overlapping an increase was seen in vehicles but not CBD. Orthogonal comparisons ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗<0.0001 n = 4.