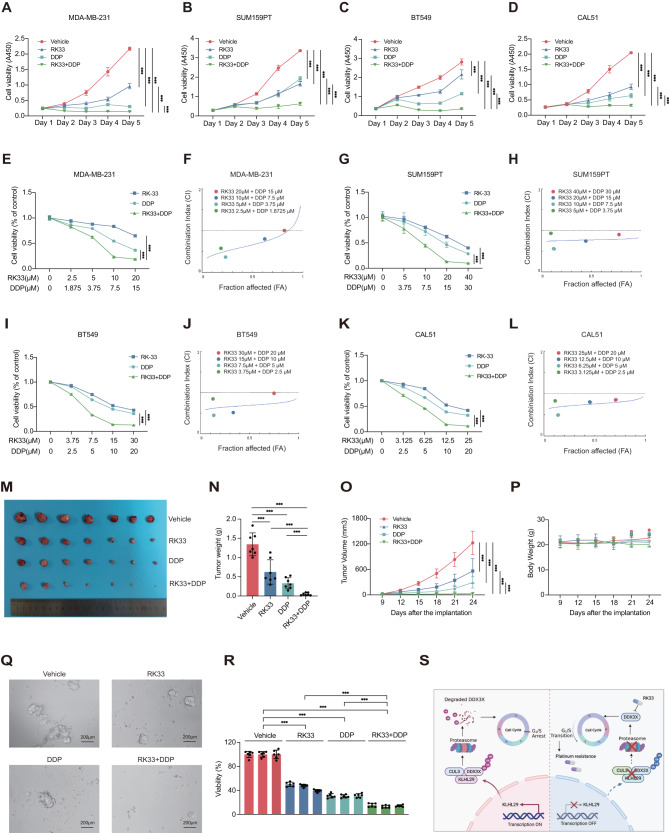
Fig. 8. The combination of DDX3X inhibitor RK33 with cisplatin suppresses TNBC progression in vitro and in vivo.
A–D Treatment with RK33 or cisplatin alone reduces cell growth of MDA-MB-231 (A), SUM159PT (B), BT549 (C), and CAL51 (D) cells compared with vehicle treatment by cell viability assays using the Cell Counting Kit-8. The combination of RK33 and cisplatin more dramatically impairs TNBC cell growth compared with each of the individual treatments. E, F RK33 and cisplatin synergistically suppress the growth of MDA-MB-231 cells. Cells were treated with combinations of agents, followed by the cell viability assays (E) and the Chou-Talalay analysis (F). G, H RK33 and cisplatin synergistically suppress the growth of SUM159PT cells. I, J RK33 and cisplatin synergistically suppress the growth of BT549 cells. K, L RK33 and cisplatin synergistically suppress the growth of CAL51 cells. M–P The combination of RK33 and cisplatin dramatically suppresses the growth of MDA-MB-231 cell-derived orthotopic xenograft tumors in BALB/c female nude mice (n = 7 mice per group). Representative tumor images (M), tumor growth rate (N), tumor weight (O) and body weight (P) are shown. Q, R The combination of RK33 and cisplatin dramatically suppresses the growth of organoids derived from TNBC patients. Representative images of organoids after drug treatment (Q), and organoid cell viability evaluated by CellTiter-Glo 3D Cell viability assay (R) are shown. S The proposed working model. KLHL29 recruits the CUL3 E3-ligase to promote ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of DDX3X, leading to the cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase. Targeting DDX3X by the small molecule RK33 sensitizes TNBC to platinum-based treatment.