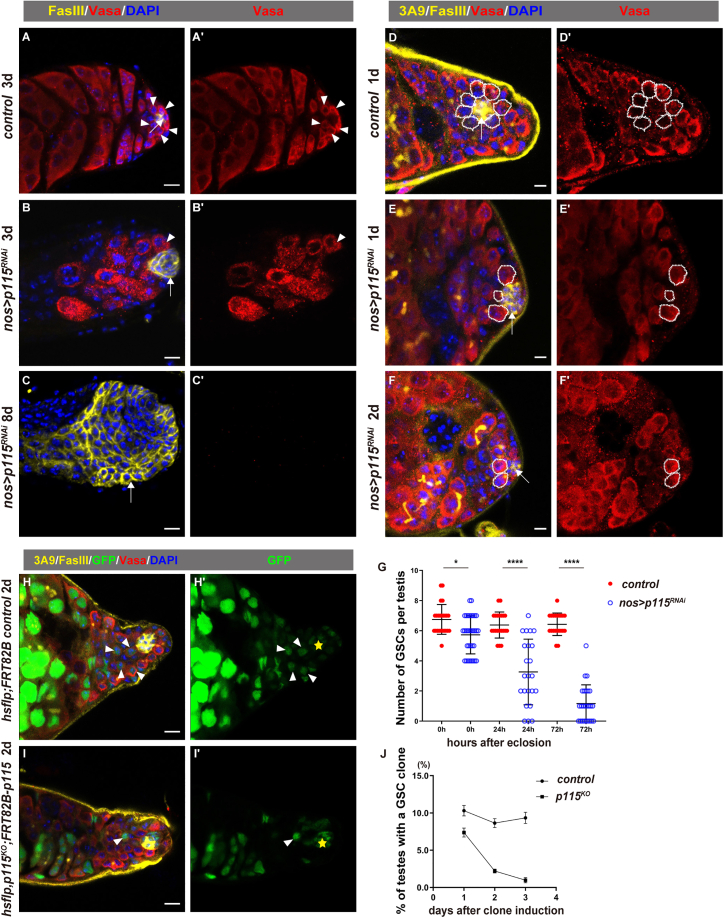
Figure 2.
p115 is required for male GSC maintenance
(A–C) Representative confocal images of adult testis with indicated genotypes. The hub is indicated by white arrows and GSCs are indicated by white arrowheads.
(D–F) Representative confocal images of adult testis with indicated genotypes. The hub is indicated by arrows and GSCs are indicated by white dotted circles. 3A9 (yellow) is stained for the fusome.
(G) Quantification of the number of GSCs per testis in testes with indicated genotypes at different time points after eclosion. Mean ± SD is shown. Control testes: n = 24 at 0 h, n = 21 at 24 h, n = 21 at 72 h after eclosion. nos > p115RNAi testes: n = 33 at 0 h, n = 23 at 24 h, n = 26 at 72 h after eclosion. Ordinary one-way ANOVA test was used. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(H) Wild-type GSC clones (white arrowheads) (2 days ACI). The hub is indicated by yellow asterisks. GFP channel is shown separately.
(I) p115KO GSC clones fail to maintain GSC fate and differentiate to spermatogonia (white arrowheads) (2 days ACI).
(J) Percentage of the testes carrying a marked WT or p115KO mutant GSC clone over time (1–3 days ACI). Three replicates, n ≥ 42. Vasa (red) is stained for germline cells, FasIII (yellow) is stained for the hub, 3A9 (yellow) is stained for the fusome and DAPI (blue) is stained for the nucleus. Scale bars, 5 and 10 μm in (A–C).