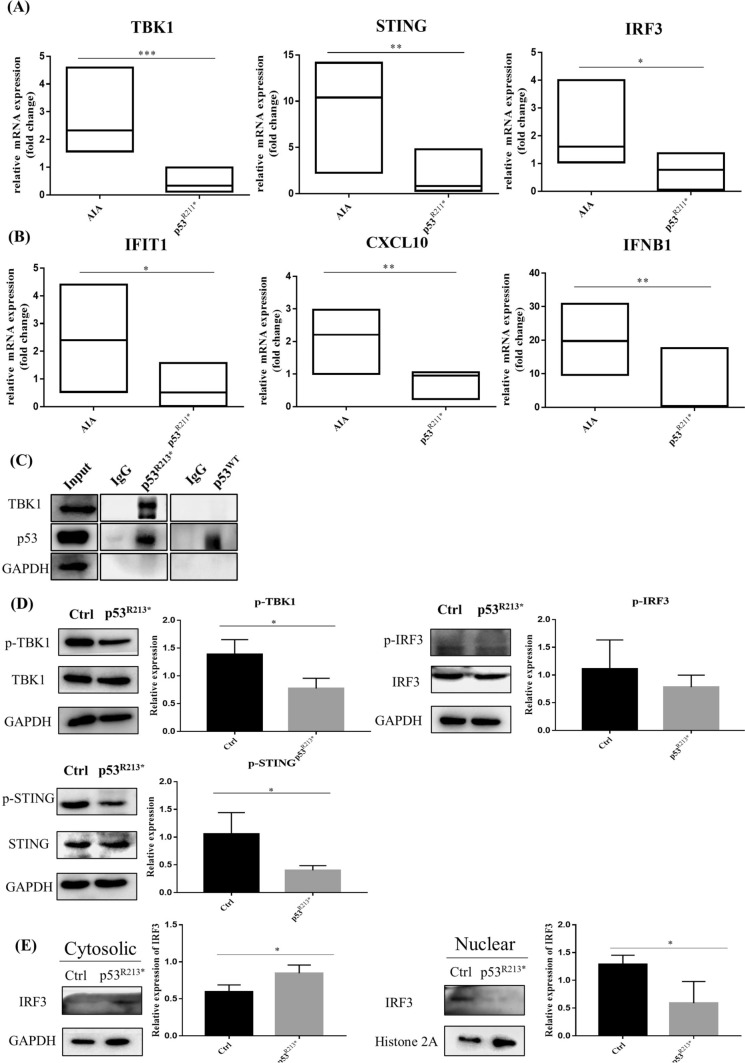
Fig. 6.
Overexpression of p53R211* suppresses innate immunity via intervention of TBK1-IRF3-STING signaling cascade. A RT-qPCR analysis of innate immune-related genes (TBK1, STING and IRF3) in the synovium of AIA rats with or without AAV-p53R211* injection. B The mRNA expressions of various IRF3-controlled inflammatory cytokines (IFIT1, CXCL10 and IFNB1) in the synovium of AAV-p53R211*- and AAV-EGFP-injected AIA rats. C The interaction of human p53R213* mutant with TBK1 protein in RAFLS. The p53R213* and p53WT plasmid DNA were transfected into RAFLS cell line for 48 h and was immunoprecipitated from whole cell lysates. The cell lysates and immunoprecipitated proteins (IP) were then analyzed by Western blotting. D Overexpression of human p53R213* mutant suppressed the phosphorylation of TBK1, IRF3 and STING in RAFLS. RAFLS were transfected with p53R213* plasmid DNA for 48 h. Cell lysates were collected and analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against p-TBK1, p-IRF3 and p-STING. The bar charts show the quantification of target protein expressions versus GAPDH expression from three independent experiments using ImageJ software. E Western blot analysis of IRF3 expression in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions from RAFLS with or without the overexpression of p53R213* mutant. GAPDH and Histone 2A were used as loading controls for the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with AIA control group or mock transfected control cells