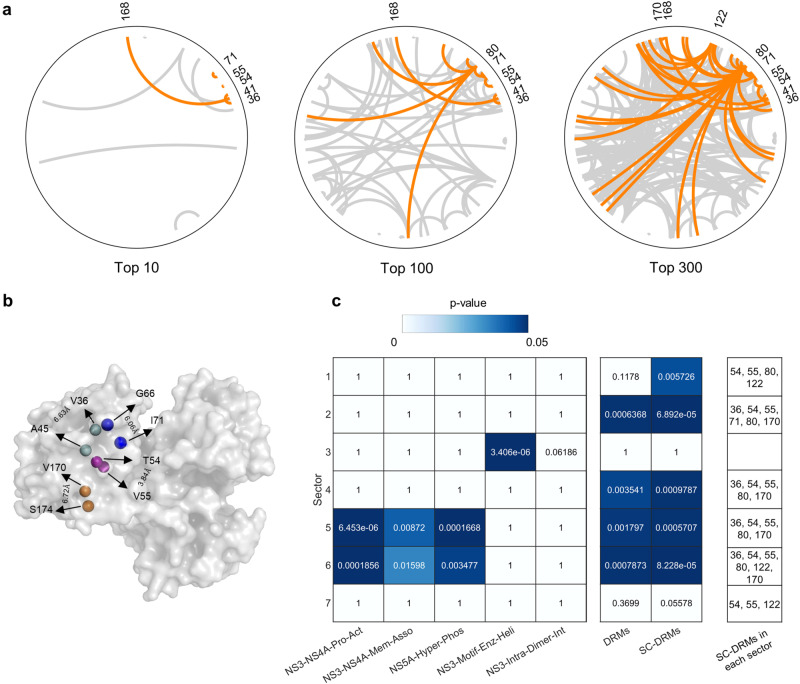
Fig. 2. Identification of SC-DRMs and their significance.
a Network of interactions between top 10/100/300 ranked mutations (ranked by the values of -J from Eq. (1)). Interactions linking at least one DRM are shown orange, and links between non-DRMs are shaded in gray. b Pairs of interacting residues involving SC-DRMs that are in contact based on the crystal structure of the NS3 protein (PDB ID: 4B6E [10.2210/pdb4b6e/pdb]). The carbon-alpha atoms of each pair of residues are shown as colored spheres, and the distance between each pair is also labeled. Two residues were assumed to be in contact if their carbon-alpha atoms were <8 Å apart. c Inferred NS3 sectors and their association with SC-DRMs. Sectors (listed in Supplementary Table 1) were inferred using the GUI implementation of the robust co-evolutionary analysis approach, RocaSec37,90. The statistical significance (p-values) was determined using one-sided Fisher’s exact test. In addition to the set of residues associated with DRMs and SC-DRMs, the following known NS3 biochemical regions were provided to the Rocasec (listed in Supplementary Table 2). (i) NS3-NS4A-Pro-Act NS3-NS4A interface for protease activation40; (ii) NS3-NS4A-Mem-Asso: NS3-NS4A membrane association41; (iii) NS5A-Hyper-Phos: NS5A hyper-phosphorylation42,43; (iv) NS3-Motif-Enz-Heli: motif important for enzymatic and helicase activities in NS344; and (v) NS3-Intra-Dimer-Int: intra-dimer interface in NS3 helicase45. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.