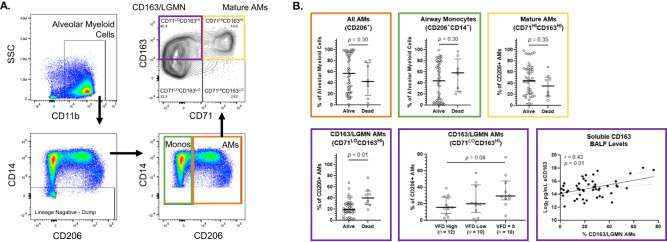
Fig. 5. CD163/LGMN Macrophages are Associated with Mortality in Acute Respiratory Failure.
We collected bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from intubated and mechanically ventilated participants (HMC Clinical Cohort) (n = 51). Table 2 shows the participant characteristics. We analyzed alveolar cells from the BAL fluid using flow cytometry. A Representative gating for identifying alveolar monocytes (Monos) (green box) and CD206+ alveolar macrophages (AMs) (orange box). We classified AMs into CD71HICD163HI (yellow box – Mature AMs) or CD71LOCD163HI (purple box – CD163/LGMN AMs) subsets based on our CITE-seq data (Fig. 4C). B The percentage of CD206+ AMs (orange box), airway monocytes (CD206+CD14+), CD71HICD163HI (yellow box – Mature AMs), and CD71LOCD163HI (purple box – CD163/LGMN) as a proportion of all alveolar myeloid cells between participants based on hospital mortality. Depicted are the individual values, median, and interquartile range of each subset as a proportion of all alveolar myeloid cells. P-values were generated with two-sided Mann-Whitney tests. CD71LOCD163HI (purple box – CD163/LGMN AMs) as a proportion of all alveolar myeloid cells between participants based on ventilator-free days (VFDs). Participants intubated > 7 days prior to bronchoscopy were excluded from this analysis. VFDs were defined as the number of days alive and free of invasive mechanical ventilation in the 21 days following bronchoscopy. VFDs were binned into tertiles. P-value was generated with Kruskal-Wallis test. Association between soluble CD163 BAL levels and the percentage of CD71LOCD163HI (CD163/LGMN AMs) as a proportion of all alveolar myeloid cells. Depicted are the individual values, linear regression line, and 95% confidence interval. P-values test whether the slope (β-coefficient) is significantly non-zero. r Pearson Correlation Coefficient.