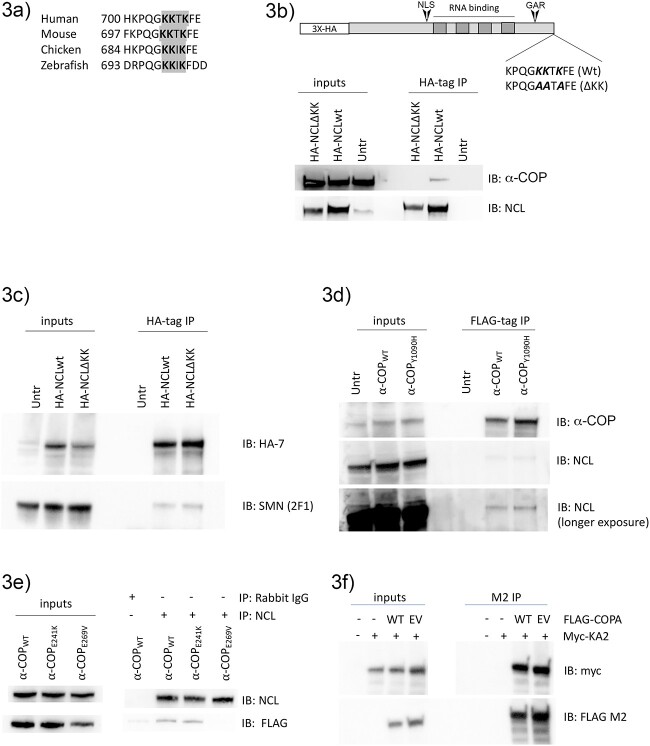
Figure 3.
The C-terminal dilysine of Nucleolin mediates interaction with α-COP. (a) An alignment of the amino acid sequence of the Nucleolin C-terminus emphasizes a highly conserved dilysine motif (gray). (b) Schematic showing HA-tagged Nucleolin with either a wildtype or mutated C-terminal dilysine (HA-NCLWT vs HA-NCLΔKK). A representative Western blot from whole cell HEK 293TT lysate shows that in immunoprecipitations using HA antibody in cells transfected with HA-NCLWT or HA-NCLΔKK, endogenous α-COP only co-precipitates with HA-NCLWT. (c) In transfected HEK 293TT cells, both HA-NCLWT and HA-NCLΔKK can co-immunoprecipitate endogenous SMN. (d) A representative Western blot from HEK 293TT cells transfected with Flag-tagged α-COPWT or α-COPY1090H. Both wildtype and the Y1090H mutant co-immunoprecipitate endogenous SMN (bottom panel shows longer exposure). (e) Representative blot showing immunoprecipitation of endogenous Nucleolin from HEK 293TT cells expressing Myc/Flag-tagged α-COP variants. Both wild-type and E241K α-COP co-immunoprecipitate with endogenous Nucleolin, but E269V α-COP did not. (f) Representative blot showing immunoprecipitation of wildtype (WT) or E269V (EV) α-COP using an antibody against the FLAG tag from cells transfected with myc-KA2. Immunoblotting with FLAG and Myc-tag antibodies shows expression of both WT and EV α-COP as well as expression of Myc-KA2 in the inputs and shows that both WT and EV co-IP’d myc-KA2 while no myc-KA2 was detected in cells without MYC-FLAG-α-COP expression.