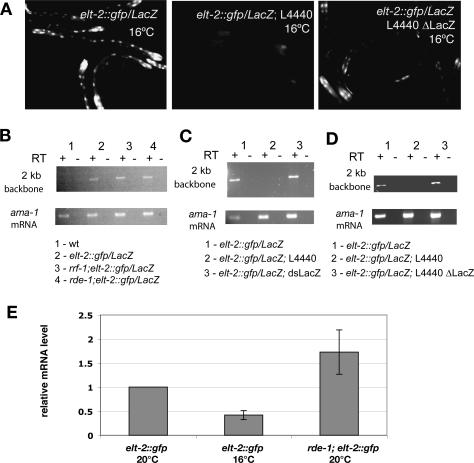
Figure 2.
The common vector backbone sequence plays a role in L4440-dependent silencing of elt-2::gfp/LacZ transgene. (A, left) elt-2::gfp/LacZ strain not exposed to L4440 at 16°C; 100% of the observed worms express GFP. (Middle) elt-2::gfp/LacZ worms on L4440 at 16°C; 100% of the observed worms have no GFP expression or very weak expression. (Right) 80%-100% of elt-2::gfp/LacZ worms on L4440-ΔLacZ at 16°C have weak GFP expression. (B-D) RT-PCR-detecting transcript from 2-kb backbone sequence in elt-2::gfp/LacZ strains; 2-kb backbone RNA is not detected in worms silenced by L4440 (C,D, lane 2). ama-1 mRNA is shown as a control for RNA samples. (E) Quantification of the relative levels of gfp/LacZ mRNA in wild-type transgenic worms at 20°C and 16°C, and rde-1(ne300) worms by real-time RT-PCR; ama-1 expression was used for internal reference. Mean values and ranges of the relative LacZ/ama-1 ratios based on three real-time RT-PCR trials are shown.