Figure 1: Glymphatic system and the spatial correlation with bvFTD.
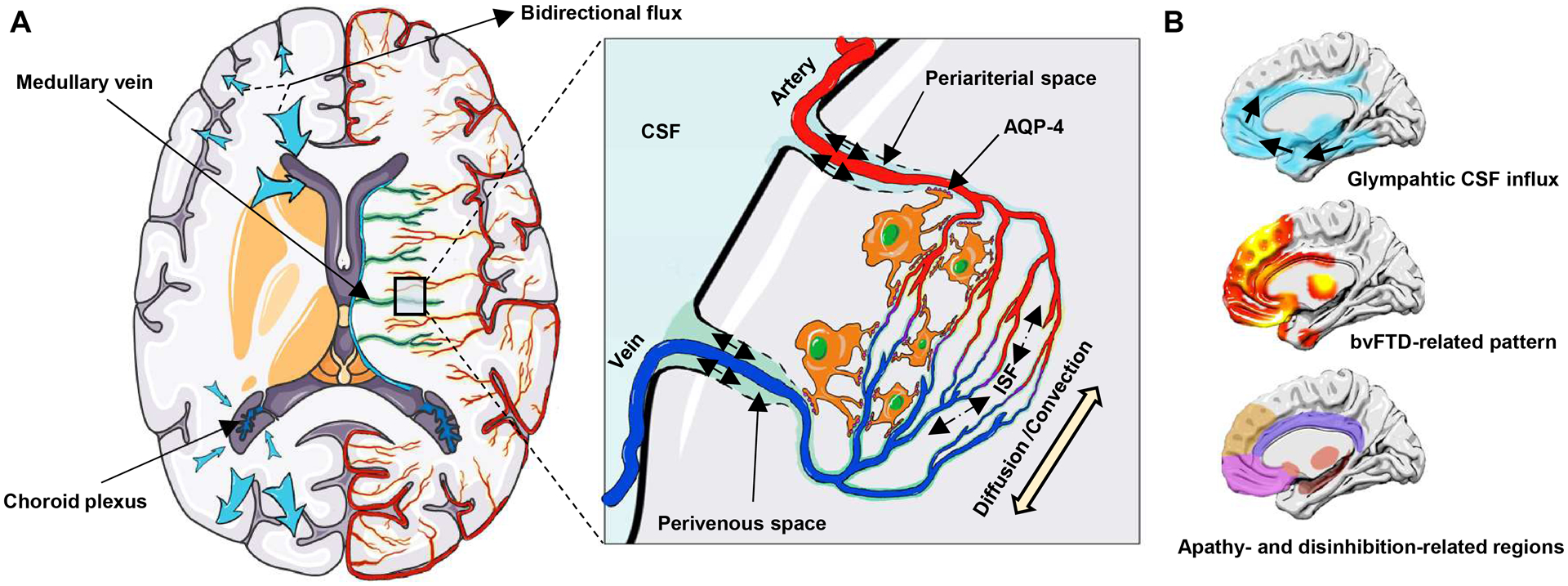
(A) Choroid plexuses secret CSF. CSF inflows from periariterial spaces to the brain parenchyma, mixes with ISF by the diffusion and convection movement, and then outflows through perivenous spaces, which is facilitated by AQP-4 water channels on astroctytic end-feet. The glymphatic pathway may have different clearance rates in different brain regions and may drive CSF-ISF bidirectionally into either the ventricles or subarachnoid space (blue arrow). (B) Spatial correlation between the glymphatic CSF influx and bvFTD related pattern, and apathy- and disinhibition-related brain regions. The bvFTD-related pattern is identified from the discovery dataset by the multivariate spatial covariance analysis based on 18F-FDG-PET imaging data. bvFTD = behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia; CSF = cerebrospinal fluid; ISF = interstitial fluid.
