Figure 1. UCP1-DTA Mice Have Reduced Body and Adipose Masses.
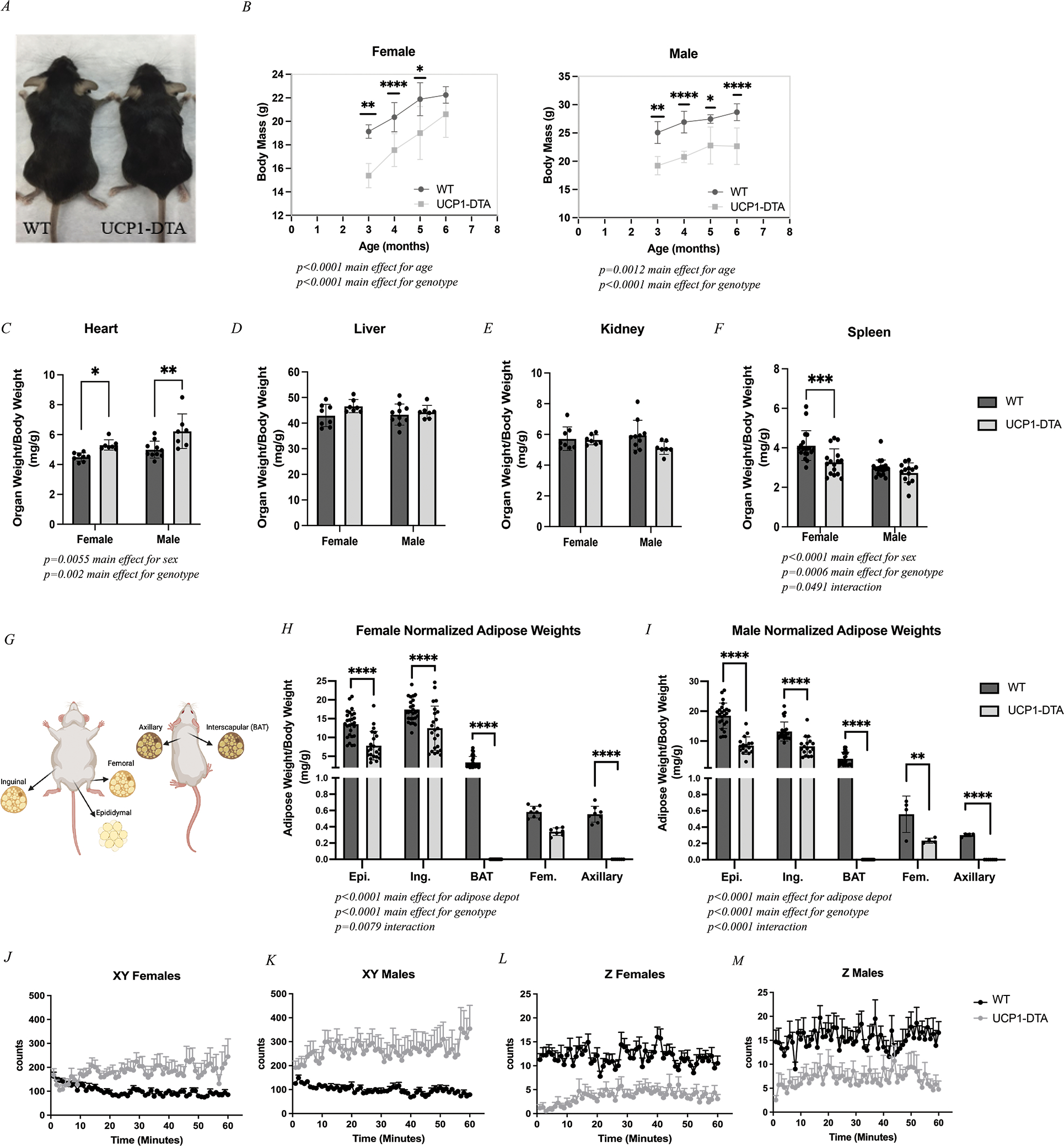
A Representative image illustrating body size differences between WT mouse (left) and UCP1-DTA mouse (right). B Body mass was significantly lower in UCP1-DTA mice across cohort ages. C Normalized heart mass is significantly higher in UCP1-DTA mice. D-E Liver and kidney analyses show no differences between sex or genotype. F Spleen mass was significantly reduced in female mice only. G Graphical anatomical depiction of six adipose depots including three classical fat depots: Epididymal (Epi.), Inguinal (Ing.), and interscapular (BAT) and two previously identified epi-muscular fat depots including Femoral (Fem.) and Axillary adipose tissue. H Normalized adipose masses in female mice show main effects for adipose depot and genotype with specific differences noted between Epi, Ing., BAT, and Axillary depots. I Normalized adipose masses in male mice demonstrate main effects for adipose depot and genotype with specific differences noted across all five fat depots between genotypes. J-M Activity data in WT and UCP1-DTA female and male mice shows that in XY directions, UCP1-DTA mice are significantly more active than WT mice, but significantly less active in the Z direction. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. Statistical significance set at p<0.05. Analyses were in Prism using two-way ANOVA or multiple, independent t-tests, or linear regression.
