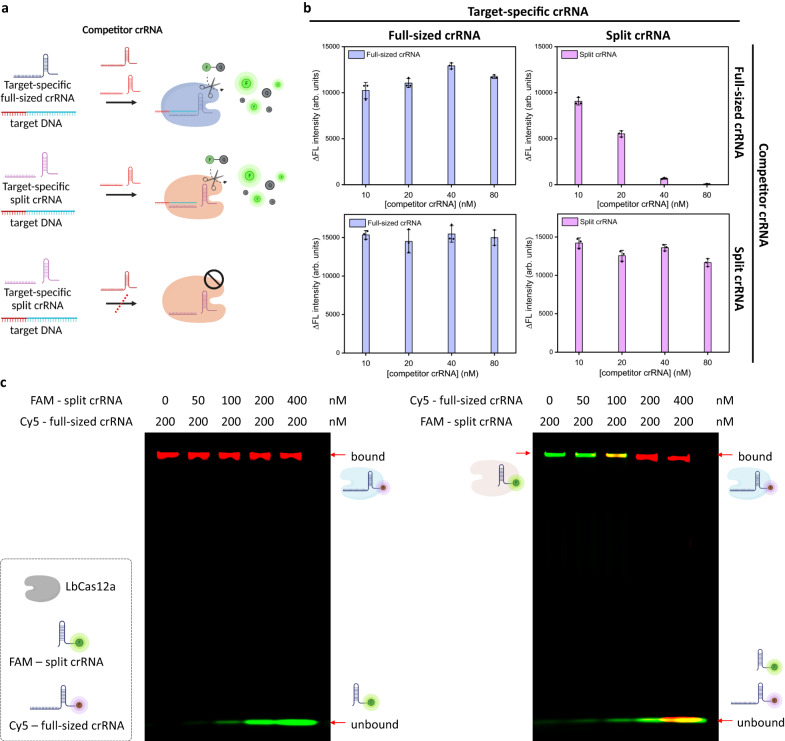
Fig. 2. Competitive CRISPR reaction between the full-sized crRNA and split crRNA.
a Effect of the competitor crRNA (full-sized and split crRNA) on the trans-cleavage reaction by target DNA and the target-specific crRNA (full-sized and split crRNA). The competitor crRNAs were designed to bind to different target sequences than the target-specific crRNAs. Illustration was created with BioRender.com. b ΔFluorescence intensity (ΔFL; FTarget DNA - FControl) of target-specific crRNA reactions in the presence of different concentrations of competitor crRNAs (10, 20, 40, and 80 nM). All the experiments were conducted in triplicate and graphs were represented by mean ± standard deviation (S.D). c Electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (Left) The concentration of Cy5-full-sized crRNA was fixed at 200 nM and the concentration of FAM-split-crRNA varied from 0 to 400 nM (0, 50, 100, 200, and 400 nM). The Cy5-full-sized crRNA remained bound to Cas12a even when the split crRNA concentration was increased. (Right) The concentration of FAM-split-crRNA was fixed at 200 nM and the concentration of Cy5-full-sized crRNA varied from 0 to 400 nM (0, 50, 100, 200, and 400 nM). As the concentration of Cy5-full-sized crRNA increased, FAM-split crRNA bound to Cas12a was replaced with Cy5-full-sized crRNA. Each Gel image was measured by Cy5 and Alexa 488 fluorescence filters respectively, and then merged. The red band represents the Cy5 fluorescence signal, and the green band represents the FAM fluorescence signal. This experiment was performed twice. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.