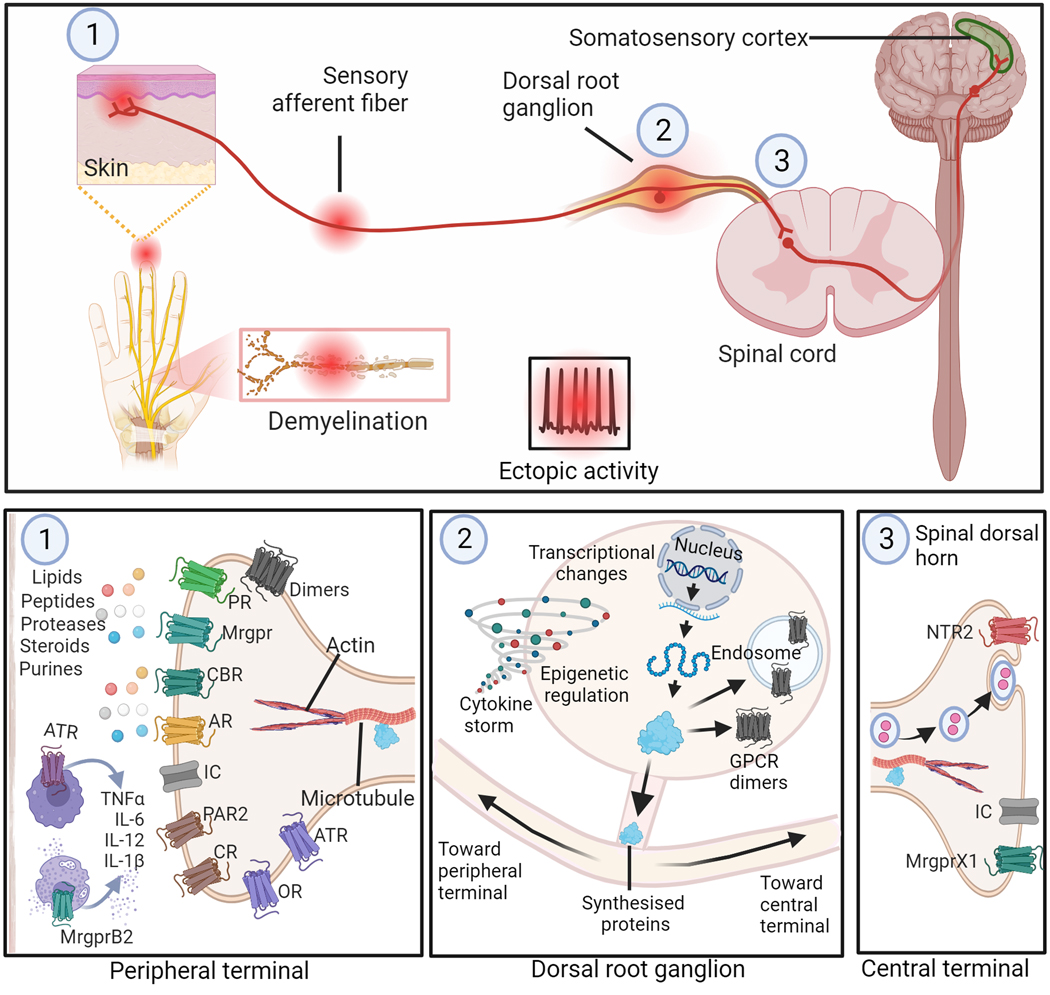
Figure 1: Possible sites on primary sensory neurons for GPCR-mediated inhibition of peripheral neuropathic pain.
Top panel depicts sites on peripheral sensory neurons (PSNs) that may develop spontaneous or ectopic activity following injury or disease affecting peripheral nerves. These sites include (1) peripheral nerve terminals near skin and site of nerve injury or demyelination, and (2) dorsal root ganglion (DRG). Activity originating at these sites are transmitted to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord where the (3) central terminals of afferent nerve fibers terminate. The bottom panel depicts potential GPCR targets at these three sites for modulation of the neuronal activity. In the periphery (1), the somatosensory insult could result in release of various biological mediators (e.g., lipids, purines, steroids, proteases, peptides lipids and cytokines) that sensitize the nociceptors. Promising GPCR targets at this site are shown. At the level of the DRG (2) transcriptomic changes may contribute to altered GPCR and ion channel expression in neurons that may result in suppressing anti-nociceptive GPCR activity and/or promoting\ pro-nociceptive GPCR functions, contributing to the pathophysiology of NP. The central terminals of PSNs (3) also offer potential targets for modulating the signals transmitted to the neurons in the spinal cord. Targeting these GPCRs at various sites along the PSNs offers opportunities for drug development for the treatment of peripheral NP. Abbreviations: OR, Opioid Receptors; AR, Adenosine Receptors; IC, Ion Channels; CBR, Cannabinoid Receptors; MrgprB2, Mas-related G-protein-coupled receptor B2; MrgprX1, Mas-related G-protein-coupled receptor X1; CR, Chemokine receptors; ATR, Angiotensin II receptors; PAR2, Protease Activated Receptor 2; PR, purinergic receptors other than ARs; NTR2, Neurotensin Receptor 2.