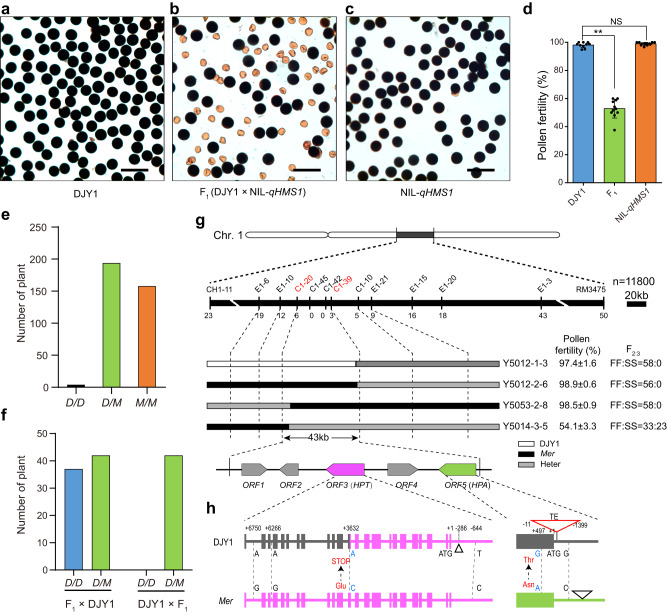
Fig. 1. Cloning of the qHMS1 locus underlying the semi-sterile pollen phenotype.
a–c Normal fertile pollens in DJY1 (a) and NIL-qHMS1 (c) and aborted pollens in their F1 plant (b), as shown by I2-KI staining to indicate starch accumulation. Scale bar, 100 μm. d Quantification of pollen fertility in DJY1, NIL-qHMS1 and their F1 shown as means ± SD (n = 10 plants). The semi-sterile pollen phenotype was seen in F1. **P = 3.47752E-9 < 0.01 by two-tailed student’s t test; NS, no significance. e Genotypic distribution at qHMS1 among a BC5F2 population. Few plants were found homozygous for the D allele, verifying the failure of its transmission through pollen. D, DJY1 allele; M, Mer allele. f Selective transmission of the Mer allele through pollen as tested in reciprocal crosses between DJY1 and F1 (DJY1/NIL-qHMS1). Plants derived from the crosses were genotyped using molecular markers to distinguish origin of the qHMS1 alleles. g qHMS1 was anchored to a 43-kb region on chromosome 1. Numbers under the black bar indicate recombinants between markers. FF, fully fertile; SS, semi-sterile; F2:3, progeny of selected F2 recombinants. Pollen fertility of these recombinants shown as means ± SD (n = 3 independent spikelets). h Genomic structure of the two candidate genes constituting a selfish genetic element. Vertical bars indicate exons. Position of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and transposon insertion is shown relative to the start codon. The two SNPs in the coding regions are highlighted in blue. TE, transposable element. Two black triangles indicate a 19-bp and a 235-bp insertion, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.