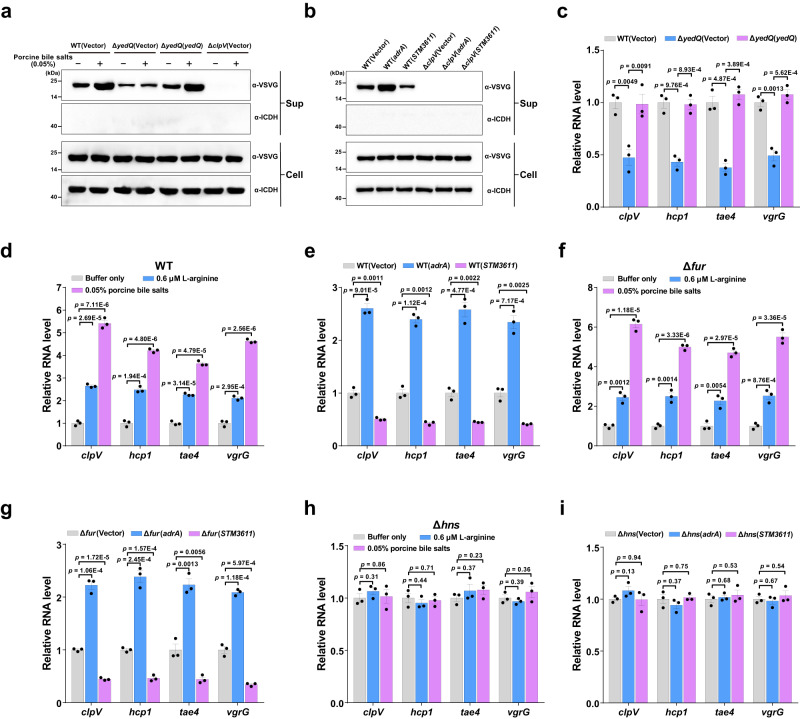
Fig. 1. Elevated c-di-GMP levels upregulate the transcription of S. Typhimurium T6SS genes via an H-NS-dependent pathway.
a The activity of the SPI-6 T6SS is enhanced by bile salts in the wild-type (WT) strain, but not in ΔyedQ. Western blot analysis of Hcp1 with a C-terminal vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSVG) tag was performed in cell pellet (Cell) and concentrated supernatant (Sup) from S. Typhimurium strains carrying a plasmid expressing Hcp1-VSVG. An antibody against isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) is used as a loading control. b The T6SS activity of WT S. Typhimurium is modulated by overexpression of adrA or STM3611. c qRT-PCR analysis of T6SS gene expression in the WT, ΔyedQ mutant and complemented strains. d, e qRT-PCR analysis of T6SS gene expression in WT S. Typhimurium stimulated by L-arginine or bile salts (d) or its derivatives overexpressing adrA or STM3611 (e). f, g qRT-PCR analysis of T6SS gene expression in Δfur stimulated by L-arginine or bile salts (f) or its derivatives overexpressing adrA or STM3611 (g). h, i qRT-PCR analysis of T6SS gene expression in Δhns stimulated by L-arginine or bile salts (h) or its derivatives overexpressing adrA or STM3611 (i). a, b Blots shown are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. c–i Gene expression levels were reported as fold change relative to that of the WT (c–e), Δfur (f, g) or Δhns (h, i) without stimulation or gene overexpression. Data are mean ± SD of three biological replicates. Two-sided, unpaired Student’s t-test was used for statistical analyses, and p < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistically significant differences. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.