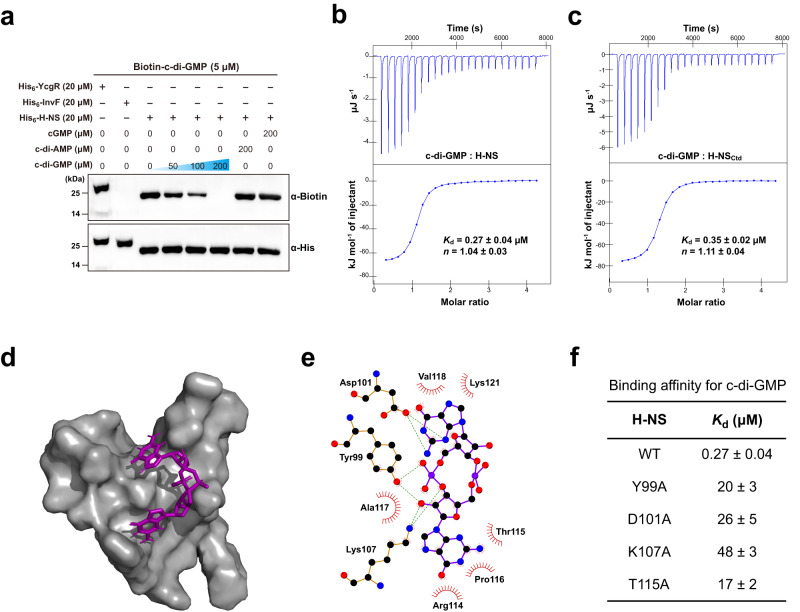
Fig. 2. Assays for specific interaction between H-NS and c-di-GMP.
a The UV-crosslinking assay detecting binding of His6-H-NS to biotinylated c-di-GMP. His6-YcgR was used as a positive control while His6-InvF was employed as a negative control. A competitive experiment was performed by the addition of unlabeled c-di-GMP, c-di-AMP or cGMP to the reaction mixtures. Reaction samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto the membrane and probed with streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (anti-biotin antibody) (top). The amounts of each protein that had been transferred to the membrane were also determined by western blot with the anti-His antibody (bottom). The blots shown are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. b, c c-di-GMP binds to H-NS (b) and H-NSCtd (c) with high affinity. Data shown are one representative of three independent experiments with similar results, with Kd and complex stoichiometry (n) presented as mean ± SD. d Surface representation of the structural model of H-NSCtd in complex with c-di-GMP. c-di-GMP is shown as purple sticks. e Schematic of the predicted contacts between c-di-GMP and H-NSCtd. Potential hydrogen bonds are indicated as green dashed lines. f Binding of c-di-GMP to wild-type (WT) H-NS and its mutants. The binding affinity was measured by ITC. The Kd values are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.