FIGURE 1.
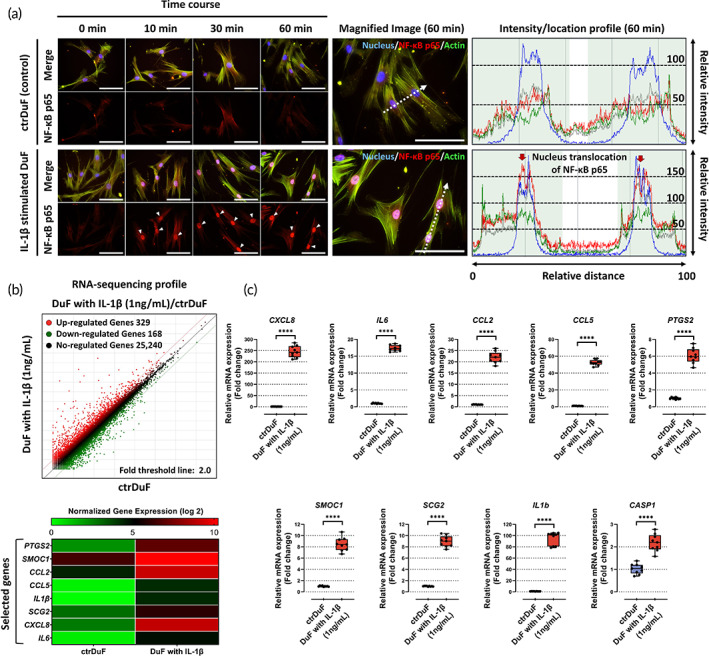
Activation of the NF‐κB signaling pathway and the expression of angiogenic genes and chemokines in IL‐1β‐stimulated DuF. (a) Fluorescence images and quantitative results show the translocation of NF‐κB p65 protein, which is a subunit of NF‐κB complex (p65/p50 complex), into nucleus in IL‐1β‐stimulated DuF. Red arrow indicates the preferential distribution of this protein in the nucleus. Its nucleus translocation in the nucleus functions as a transcription factor that induces the encoding of inflammatory and catabolic genes. Scale bar = 100 μm. (b) Using RNA‐seq analysis, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in DuF with or without IL‐1β are illustrated as a scatter plot. Normalized gene expression (log 2) > 4.0 and adjusted p value <0.05 were used as the cutoff to identify DEGs. Heatmaps show the expression of a class of pro‐angiogenic and chemotactic genes in different groups. Based on these results, nine genes were selected as target factors in this study. (c) qRT‐PCR analysis of the expression of the selected genes and CASP1 in DuF with or without IL‐1β. The results show significantly higher expression of all genes and CASP1 in IL‐1β‐stimulated DuF compared with those in naïve DuF. The values are reported as the mean ± standard error of nine independent experiments. ****p < 0.0001 compared to naïve DuF.
