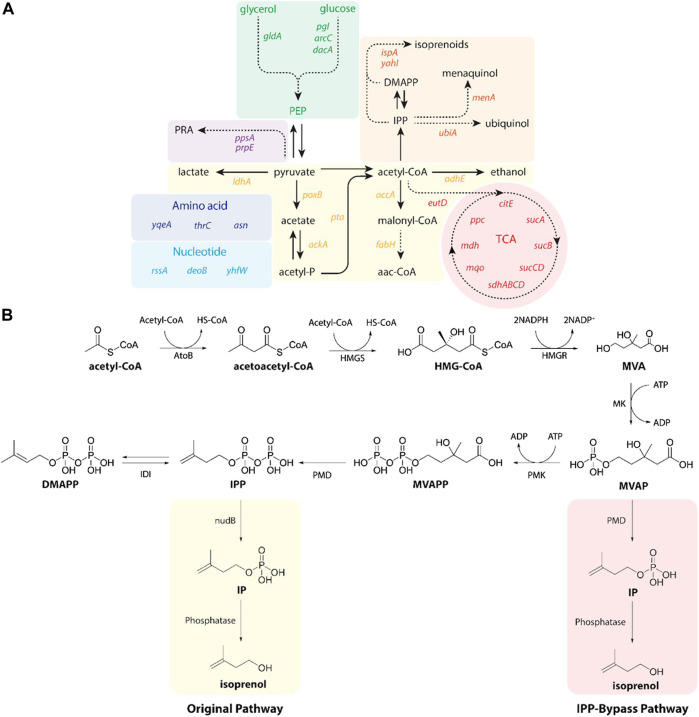
FIGURE 2.
(A) A pathway map of gene knockdown targets for redirecting metabolic flux toward isoprenol production using CRISPRi. Pathways and relevant genes are colored as follows: green box, glycolysis; purple box, amino acids pathway; violet box, propionic acid pathway; light blue box, nucleotides pathway; yellow box, organic acids pathway; orange box, isoprenoids pathway; red box, TCA cycle pathway. PRA, propionic acid; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; TCA, citric acid cycle. (B) Original (yellow box) and IPP-bypass (red box) MVA pathways for isoprenol production. The MVA pathway converts acetyl-CoA to IPP in 6 enzymatic steps with subsequent isomerization to dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). Dephosphorylation of IPP and DMAPP by nudB, a promiscuous E. coli phosphatase, produces isoprenol and prenol, respectively. The IPP-bypass pathway was proposed in this study for direct decarboxylation of mevalonate monophosphate (MVAP) to isopentenyl monophosphate (IP) followed by dephosphorylation by an endogenous phosphatase. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AtoB, acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA; HMGR, HMG-CoA reductase; HMGS, HMG-CoA synthase; IDI, isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase; IP, isopentenyl monophosphateIPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; MK, mevalonate kinase; MVA, mevalonate; MVAP, mevalonate monophosphate; MVAPP, mevalonate diphosphate; PMD, mevalonate diphosphate kinase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase.