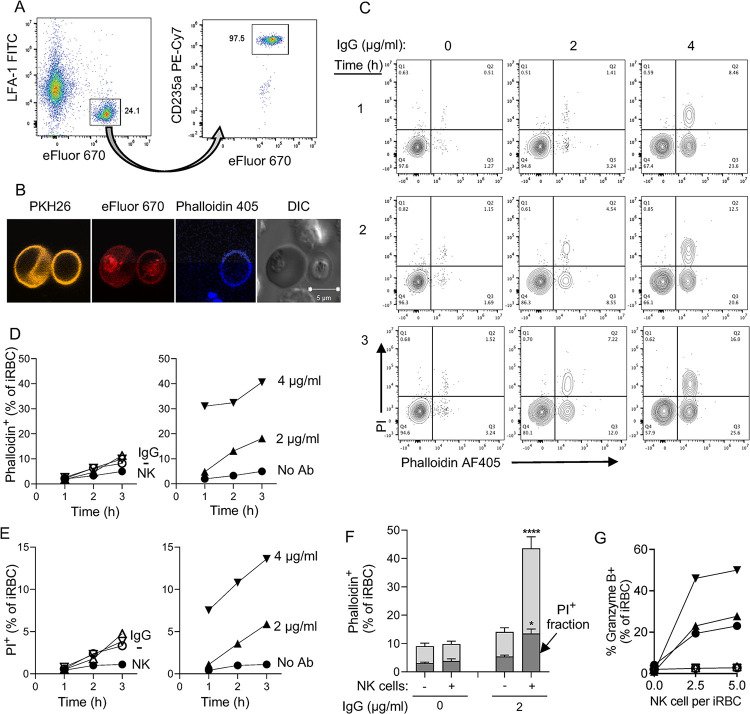
Fig 2. Sequential damage to P.f.-infected RBC and to the parasite during NK-dependent ADCC.
(A) Gating strategy to identify primary NK cells and 3D7 P.f.-iRBC mixed at a 3 to 1 ratio. iRBC were prelabelled with eFluor 670. After incubation with NK cells, iRBC were stained with an Ab to glycophorin A (CD235a PE-Cy7) and NK cells were stained with an Ab to the integrin LFA-1 (FITC). (B) Immunofluorescence image of iRBC stained with the membrane dye PKH26 (yellow) and the primary amine dye eFluor 670 (red) and incubated with NK cells for 3 hours in the presence of F-actin binding Phalloidin-AF405 (blue). The DIC image shows an intact iRBC (left) and a translucent ghost iRBC (right). Two unstained NK cells are visible (top and bottom). (C) NK cells and iRBC were incubated at a ratio of 3:1 for up to 3 hours in the presence anti-RBC IgG, as indicated. Damaged iRBC were detected with Phalloidin AF405 and damaged parasites identified with DNA binding of propidium iodide (PI). Results are representative of seven experiments. (D) Time-, Ab-, and NK-dependent damage to iRBC detected by phalloidin staining. Control iRBC incubated with nothing (-), Ab alone (IgG), or with NK cells alone (NK) are shown on the left. (E) NK-dependent damage to parasites was determined by PI staining. Controls in the left panel are as described in (D). (F) Data from seven independent experiments with NK cells from different donors performed as in D and E shown as the proportion of iRBC that became Phalloidin-AF405+ and of intra-erythrocytic parasite damage detected as phalloidin and PI double-positive events (darker shading). Samples were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (-) of NK cells and of 2 μg/ml anti-RBC IgG for 3 hours. Standard error of the mean: * p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (G) Granzyme B reporter assay performed with iRBC after incubation with NK cells in the presence of 1 μg/ml IgG. Prior to analysis, NK–iRBC conjugates were disrupted by addition of 5mM EDTA. Residual conjugates were gated out using forward scatter parameters (FSC >600) on the flow cytometer. eFluor 670-labeled iRBC were mixed with primary NK cells in the presence or absence of IgG for 1 h at 37°C. Granzyme B substrate was then added to the cells and eFluor670+ granzyme B+ iRBC were quantified by flow cytometry. Filled symbols represent independent experiments with NK cells from three individual donors. Open symbols represent samples incubated in the absence of IgG.