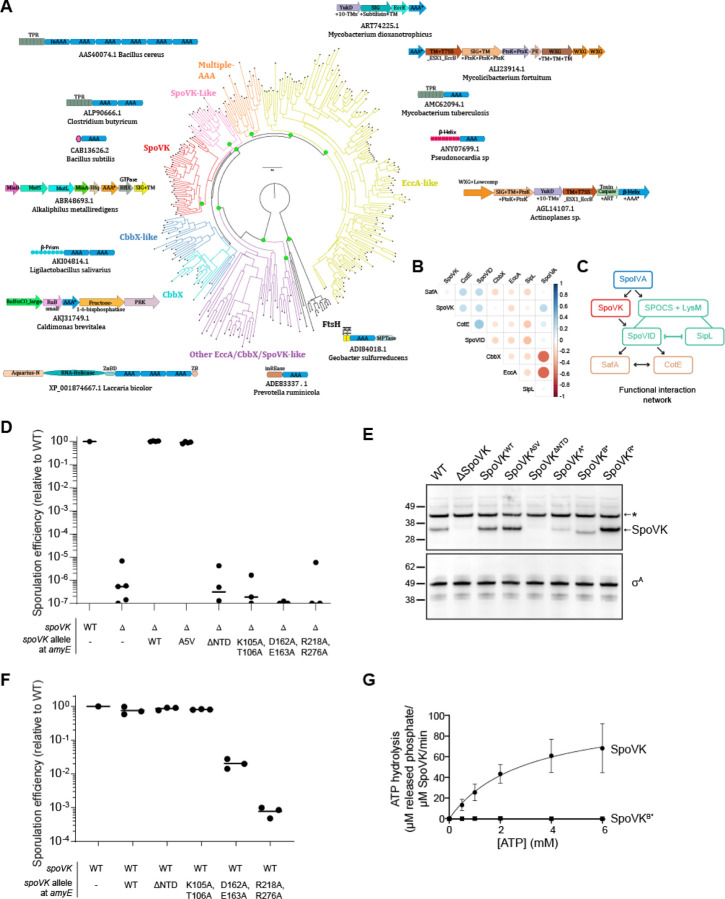
Figure 3. SpoVK is a functional triple AAA+ protein.
(A) Phyletic analysis of the SpoVK-EccA-like clade. A phylogenetic tree of a representative set of AAA+ domains in the SpoVK-EccA-like clade is shown. The tree shows the relationship between the SpoVK, SpoVK-like, CbbX, CbbX-like, and EccA-like families and the closest outgroup FtsH. Branches are colored according to the families. Select operonic arrangements or domain architectures of proteins are shown and placed near the branch of the tree in which they or their orthologs occur. Each arrow in the operon is a gene coding for the protein. The accession and organism of the AAA+ containing protein in the operon, marked with an asterisk, is shown below each operon or domain architecture. ZnBd: zinc-binding. (B) Correlation matrix of SpoIVA, SpoVK, CbbX, EccA, SafA, and SPOCS domain-containing proteins SpoVID, CotE, and SipL/DUF3794 was computed from their phyletic pattern vectors. Color intensity and the size of the circle are proportional to the correlation coefficient. (C) A correlation network of SpoIVA, SpoVK, CbbX, EccA, SafA, and SPOCS domain-containing proteins SpoVID, CotE, and SipL/DUF3794 was computed from this matrix and the phyletic pattern vectors. The nodes and edges are colored as per their functional subgroup in the sporulation system. The arrowheads indicate positive correlations and point from the phyletically more widespread to the less widespread proteins. The flat heads indicate negative correlations. Lines indicate a split in a functionally equivalent family into sub-groups (e.g., SipL and SpoVID).
(D) Sporulation efficiencies, determined as resistance to heat, relative to WT (PY79). Strain genotypes at the spoVK locus are indicated below the graph; amyE is an ectopic chromosomal locus used to complement the spoVK deletion strain with the indicated allele of spoVK. Bars represent mean values. Strains: PY79, TD520, TD513, TD514, TD574, TD575, TD576, and TD578. (E) Immunoblot of cell extracts of sporulating B. subtilis using antiSpoVK or anti-σA antisera, from cells harvested at 4 h after induction of sporulation. Strains: PY79, TD520, TD513, TD514, TD574, TD575, TD576, and TD578. (F) Sporulation efficiencies, determined as resistance to heat, relative to WT (PY79). Strain genotypes at spoVK locus are indicated below the graph; amyE is an ectopic chromosomal locus used to produce a merodiploid strain containing two alleles of spoVK. Bars represent mean values. Strains: PY79, TD597, TD598, TD599, TD600, and TD602. (G) Saturation curve for ATP hydrolysis by purified SpoVK and SpoVK variant harboring a disrupted Walker B motif (D162A, E163A). Purified SpoVK or SpoVKD162A, E163A was incubated with increasing concentrations of ATP, and nucleotide hydrolysis was assayed by measuring the generation of free phosphate. Data were fit to the Michaelis-Menten enzyme saturation model.