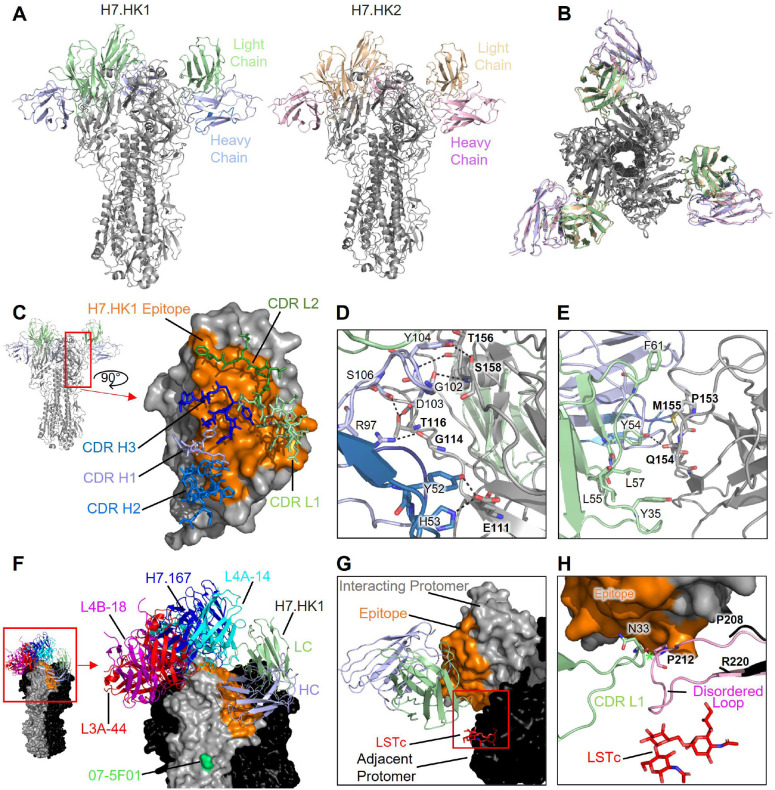
Fig. 2. Structural analysis of H7.HK1 and H7.HK2 in complex with H7 HA trimer.
(A) Cryo-EM structures of H7.HK1 and H7.HK2 bound to H7 HA in the head region. (B) Top view of alignment of H7.HK1 and H7.HK2 complex structures. (C) Surface presentation of the H7.HK1 epitope (orange) on H7 HA1, with interacting CDRs shown. (D) H7.HK1 heavy chain forms seven hydrogen bonds and one salt bridge with H7 HA1. (E) H7.HK1 light chain forms one additional hydrogen bond with H7 HA1, and the interactions are stabilized by hydrophobic residues on the periphery of the light chain interface. (F) Modeling published structures of H7 HA1-binding antibodies (PDB: 6II4, 6II8, 6II9, 5V2A) onto the H7.HK1 bound structure, with an escape mutation R47K (green) reported for mAb 07–5F01. (G) Modeling the binding site of human receptor analogue LSTc (red) based on a previous crystal structure (PDB: 4BSE) onto H7 from the H7.HK1 complex, showing that H7.HK1 does not compete with sialic acid on the adjacent protomer (black). (H) Alignment of the H7.HK1 complex with a previous crystal structure of H7 (PDB: 4BSE) shows that the 220-loop (pink) required for sialic acid binding (G209-G219) is disorder in the complex structure and would clash with the H7.HK1 light chain if it were present. Green asterisk symbol denotes the <2 Å clash between the CDR L1 N33 and the predicted location of P212 on HA1.