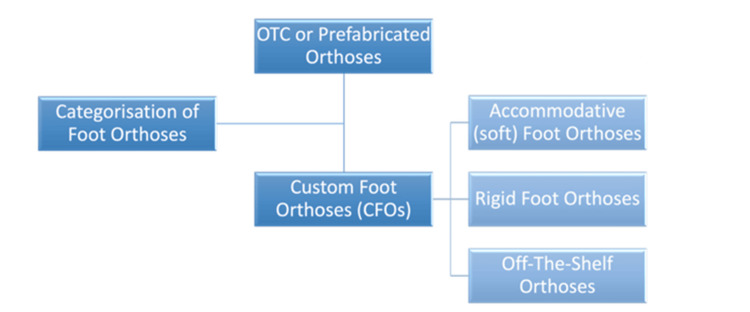
Figure 2. Broad categorisation of foot orthoses.
Over-the-counter (OTC) or prefabricated orthoses: prescribed by clinicians for multiple ailments, they are standardised, readily available, and relatively cheap; however, they can be less durable.
Custom foot orthoses (CFOs): custom-made and individualised, they are more durable but can be expensive [2]. CFOs can be further subdivided into:
a. Accommodative (soft) foot orthoses: provide a cushioning effect and act as shock absorbers; they are prescribed for conditions resulting in fixed deformities and insensate feet.
b. Rigid foot orthoses: used to control/decrease motion in conditions resulting in flexible deformities.
c. Off-the-shelf orthoses: prescribed in conditions resulting in pain and discomfort, without ulcers or neuropathy, to provide cushioning and shock attenuation.
Image created by the authors.