FIGURE 6.
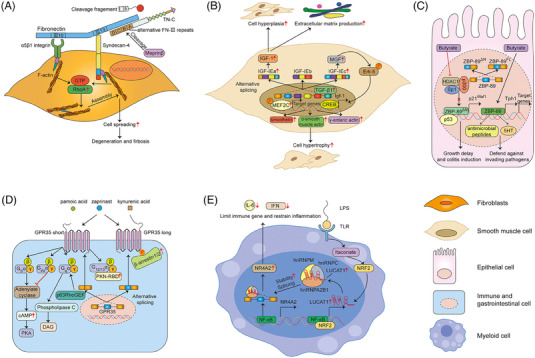
AS regulates fibrosis and other risk factors in the pathogenesis of IBD. (A)TN‐C that contains an alternatively spliced FNIII repeats A1–D interferes the FN/syndecan‐4 interaction, resulting in actin stress fibre assembly and cell spreading. (B) The splicing isoforms of IGF‐I induced by TGF‐1 are involved in cell hyperplasia, cell hypertrophy and extracellular matrix production in smooth muscle cell. (C) Two ZBP‐89 splice isoforms (ZBP‐89FL and ZBP‐89DN) regulate biological functions in epithelial cells. ZBP‐89FL tends to protect against chronic colitis, while ZBP‐89DN renders the colonic mucosa more susceptible to colitis. (D) Two distinct variants of GPR35 (GPR35 long and short) implicate in gut‐related diseases, and these two variants differed only in the length of their extracellular N‐termini by 31 amino acids. The short isoform can activate different major G proteins, while the presence of GRP35 long plays a positive modulator for arrestin recruitment. (E) LUCAT1 controls the splicing and stability of anti‐inflammatory NR4A2, thereby contributing to the suppressing effects of interferons and inflammatory mediators.
