FIGURE 1.
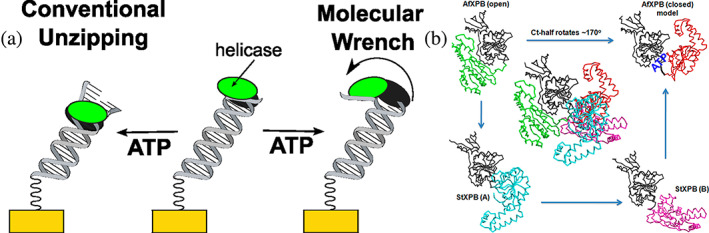
(a) An illustration of conventional and molecular wrench helicase mechanisms for Archaeoglobus fulgidus helicase (AfXPB). The domains of AfXPB are colored green and gray. (b) Structural comparison of AfXPB and helicases from Sulfolobus tokodaii (StXPB2). Center: The AfXPB structure (PDB: 2FZ4 & 2FZL) is superimposed with the two StXPB2 structures over the damage recognition domain and helicase domain1 (gray). For AfXPB, the C‐terminal halves are shown as green in the open conformation and red in the closed conformation. For StXPB2 (PDB: 5TNU), two open crystal structures are shown. The C‐terminal halves are shown as cyan for structure A and magenta for structure B. The AfXPB closed conformation is a computational model, and the ATP‐binding groove is highlighted. Reprinted (adapted) with permission from Anal Chem. 90(3):2178–2185. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.
