FIGURE 1.
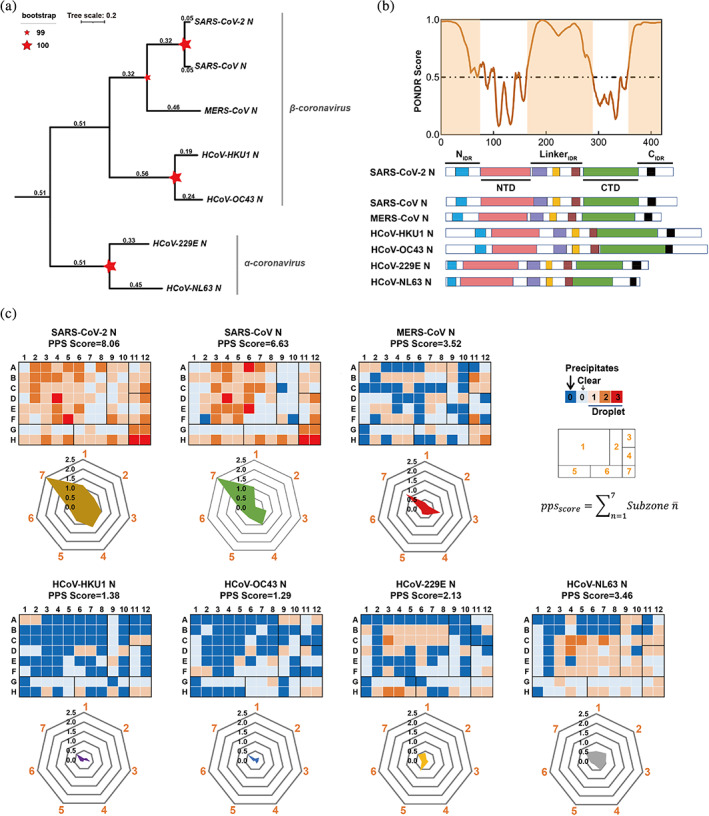
LLPS is a general property shared by N proteins from seven different human coronavirus. (a) The phylogenetic tree was generated from primary sequence of the seven homologous N proteins by using ClusterW (http://align.genome.jp) and plotted using a Neighbor‐Joining algorithm. Tree scale and bootstrap value are indicated. (b) IDR score (SARS‐CoV‐2 N as a represent) and the domain organization of the N proteins from human coronaviruses. PONDR VSL2 predictor23 was used for calculating the IDR score. The region consisting of residues with score value higher than 0.5 is considered to be IDR (highlighted area in orange). N protein contains three putatively disordered regions: a globular N‐terminal tail, a C‐terminal tail and a central linker region. The homologous regions in the IDR are highlight in different color‐zone: AXXITFADSD motif (blue), FYAEGSXG motif (purple), SR‐rich motif(orange), LALLXL‐‐‐QQ motif (brown), K‐‐Q‐‐VTL motif (black). (c) Characterization of different N proteins from HCoVs for their LLPS abilities by HiPPS profiling. HiPPS profiles (top) and radar graph (bottom) of each N protein are shown. 50 μM of each N protein was examined at room temperature. The parameter and equation for calculating PPS scores are shown on the upper right. Values in the radar graph represent the average grades of each square sub‐zones in the HiPPS profiles; The profiling condition in sub‐zones 1–7 shown on the upper right, includes: different crowding agents (sub‐zone 1); high concentration salts (sub‐zone 2); PolyR (sub‐zone 3); PolyU/heparin (sub‐zone 4); divalent salts (sub‐zone 5); monovalent salts (sub‐zone 6); PEG 3350 gradient (sub‐zone 7). PPS score, protein phase separation score.
