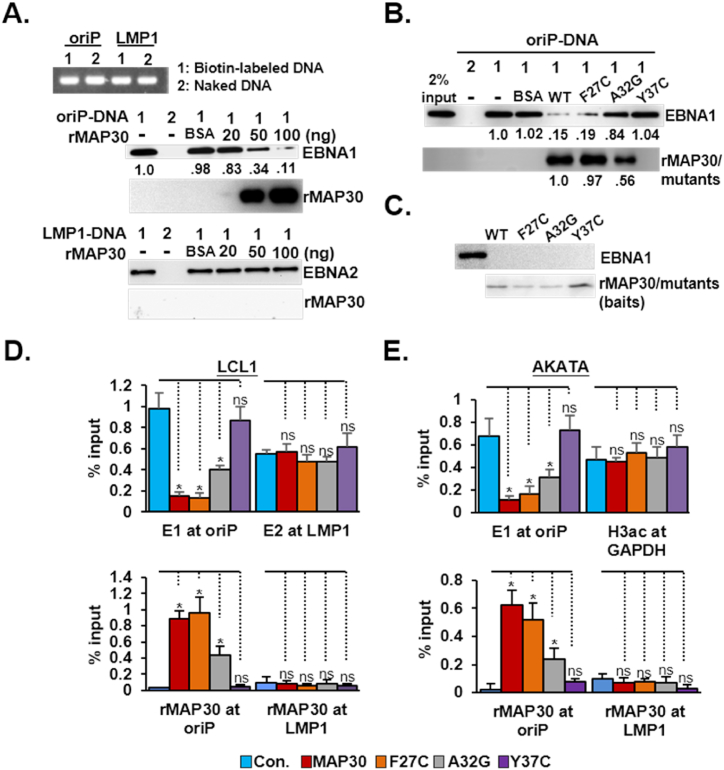
Fig. 3.
MAP30 effectively impairs EBNA1/oriP-DNA binding A). PCR-amplified biotin-labeled or naked oriP-DNA and LMP1-DNA were used to perform a streptavidin agarose-mediated DNA pulldown assay. Each DNA sample was mixed with LCL-derived cell lysates in the presence of 20, 50, 100 ng/mL rMAP30, or 100 ng BSA/mL controls. Samples were subjected to a streptavidin agarose pulldown procedure, and the amount of oriP-DNA-bound EBNA1 or LMP-1 DNA-bound EBNA2 was determined by immunoblotting analysis and quantified by ImageJ whenever necessary. B). The same experimental procedure described above was also performed with three MAP30 mutants: rF27C, rA32G, and rY37C. C) Similar amount of Ni-NTA resin bound rMAP30 or its mutants were used as bait proteins to perform an in vitro protein affinity binding assay in the context of lymphoblastoid cell lysates. The bound matrices were used to perform immune blot analysis for EBNA1, rMAP30, and its mutants, respectively. D). LCL1 cells or E) AKATA cells treated with rMAP30 or mutants were used to perform a ChIP assay using antibodies for EBNA1, EBNA2, or His-tag. Cells treated with BSA were used as the control. The amount of ChIPed DNA was quantified by qPCR and results were presented as a percentage of the input DNA. E1:EBNA1; E2:BNA2.