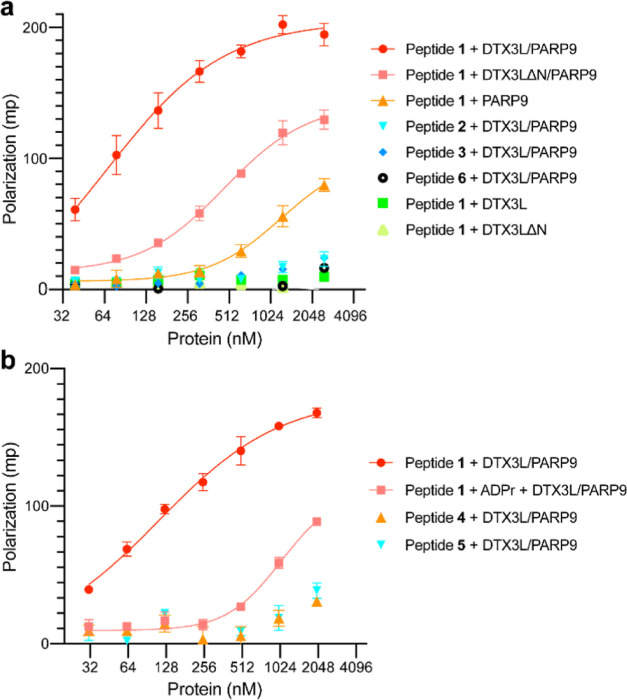
Figure 2.
Interaction of DTX3L/PARP9 and ADP-ribosylated AR peptides measured by FP assays. (a) Oligomerization of DTX3L/PARP9 is critical for recognition of a dual ADP-ribosylated AR peptide. (b) DTX3L/PARP9 binding competes with ADP-ribose (50 μM) in solution. Assays were performed in triplicate in a 384-well plate (Corning 3575) containing 50 nM fluorescently labeled AR peptide and recombinant proteins [final concentration 2500 nM in (a) or 2000 nM in (b), and 2-fold serial dilution] in a binding buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, and 2 mM DTT). The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 45 min, FP measured in a PHERAstar FSX Microplate Reader (BMG Labtech), and the binding curves were fitted for specific binding with GraphPad Prism v 9.3.1. The error bars represent the standard deviations. Dual-ADPr peptide 1: CF-RPTPC(ADPr)APLAEC(ADPr)KGSL–OH; mono-ADPr peptides 2: CF-PLAEC(ADPr)KGSL–OH; 3: CF-RPTPC(ADPr)APLA–OH; 4: CF-RPTCAPLAEC(ADPr)KGSL–OH; 5: CF-RPTPC(ADPr)APLAECKGSL–OH. Control non-ADP-ribosylated peptide 6: CF-RPTPCAPLAECKGSL–OH. Recombinant proteins were checked by SDS-PAGE as seen in Figure S10.