Abstract
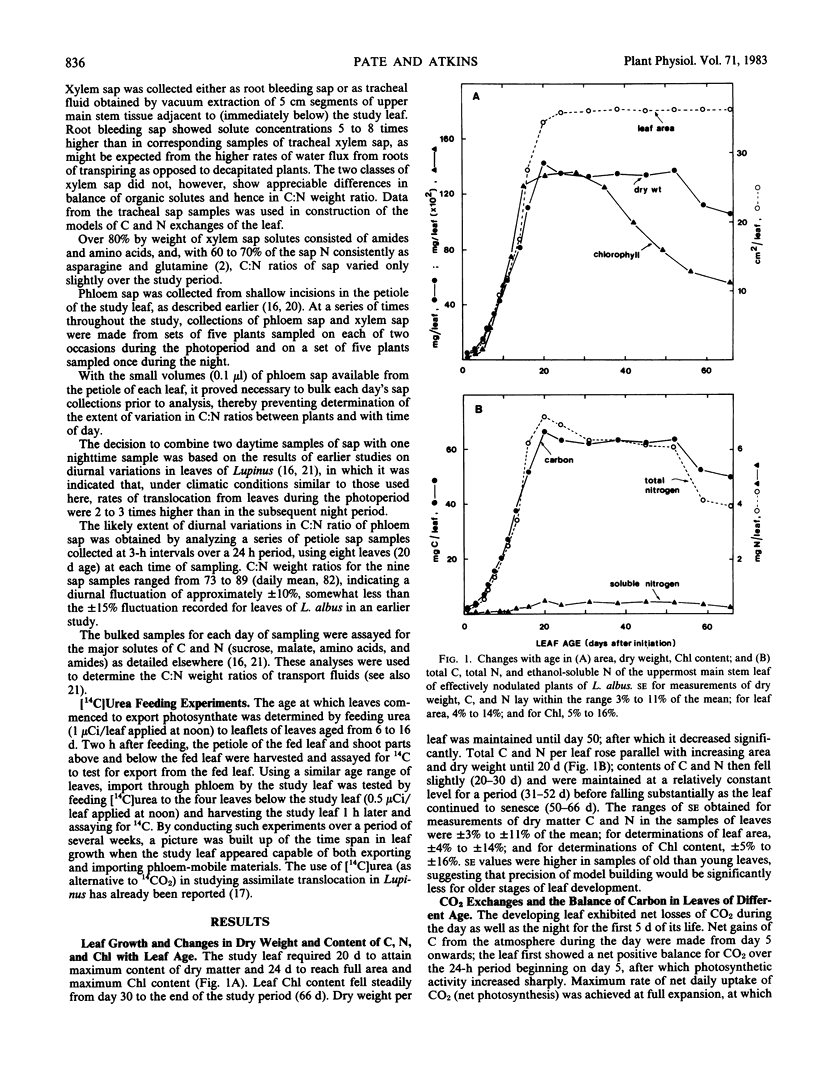
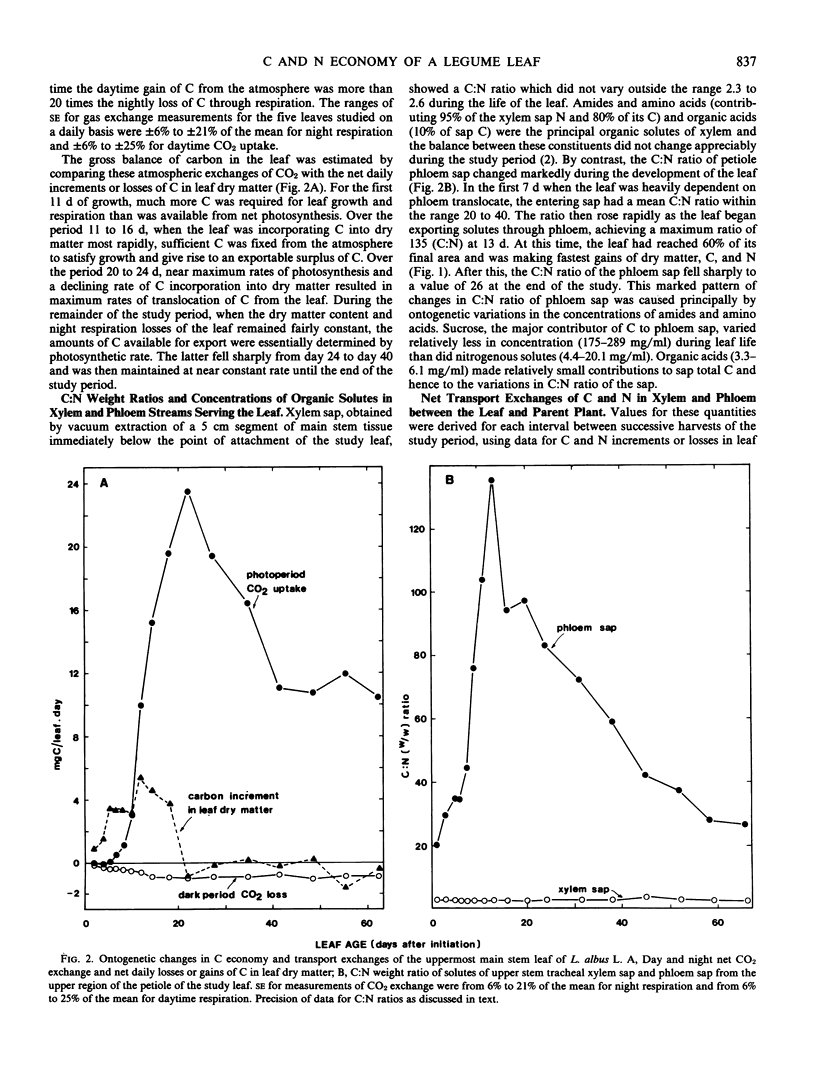
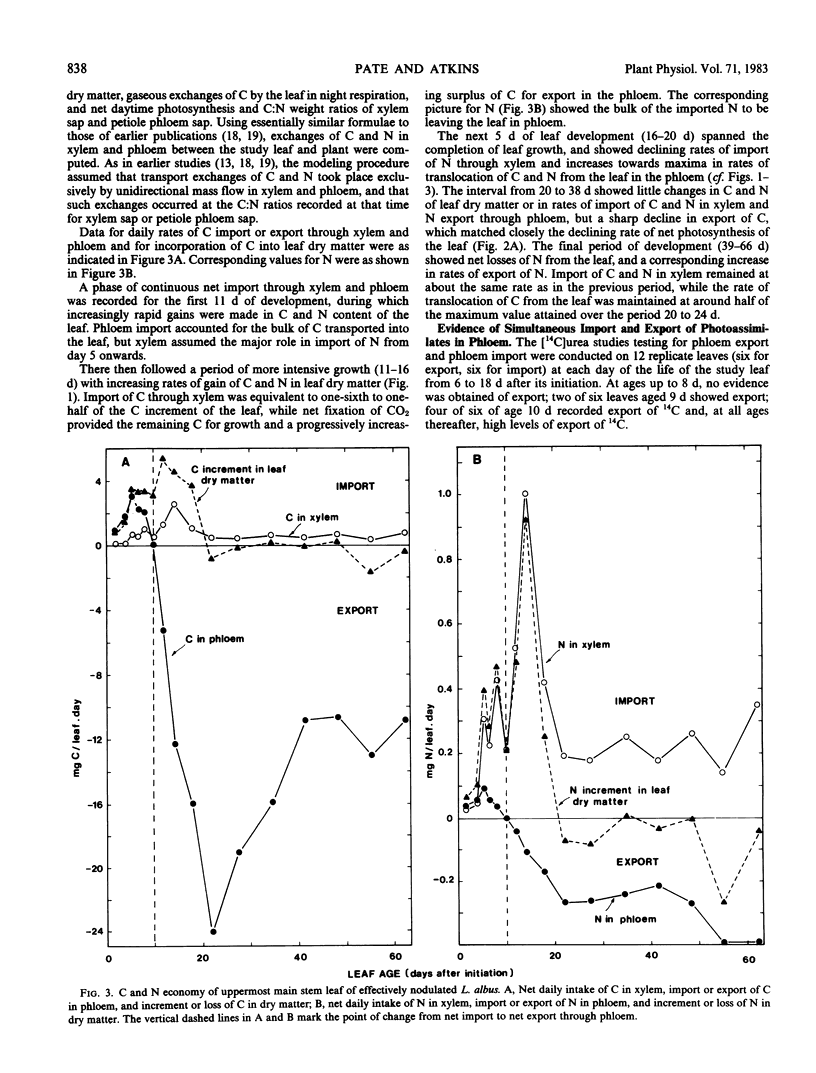
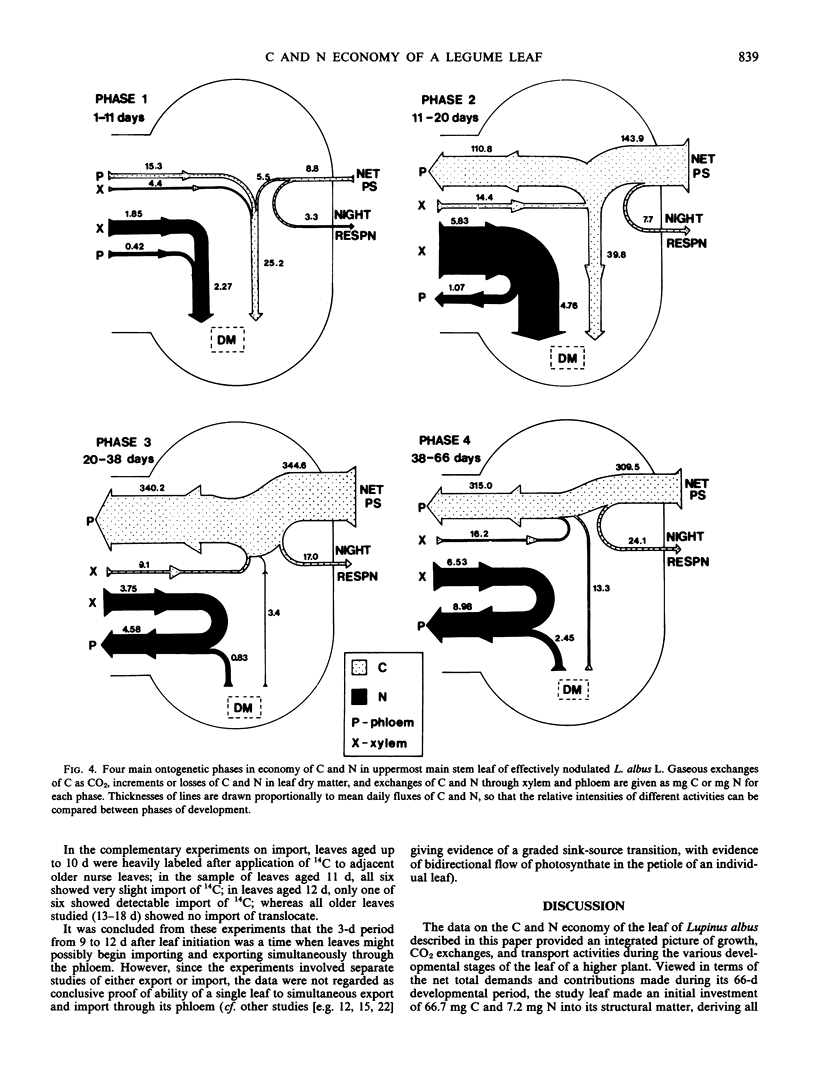
Exchanges of CO2 and changes in content of C and N were studied over the life of a leaf of Lupinus albus L. These data were combined with measurements of C:N weight ratios of xylem (upper stem tracheal) and phloem (petiole) sap to determine net fluxes of C and N between leaf and plant. Phase 1 of leaf development (first 11 days, leaf to one-third area) showed increasing net import of C and N, with phloem contributing 61% of the imported C and 18% of the N. 14C feeding studies suggested the potential for simultaneous import and export through phloem over the period 9 to 12 days. Phase 2 (11-20 days, leaf attaining maximum area and net photosynthesis rate) exhibited net import through xylem and increasing export through phloem. Eighty-two% of xylem-delivered N was consumed in leaf growth, the remainder exported in phloem. Phase 3 (20-38 days) showed high but declining rates of photosynthesis, translocation, and net export of N. Phase 4 (38-66 days) exhibited substantial losses of N and declining photosynthesis and translocation of C. C:N ratio of xylem sap remained constant (2.3-2.6) during leaf life; petiole phloem sap C:N ratio varied from 25 to 135 over leaf development. The relationships between net photosynthesis and N import in xylem were: phase 1, 4.8 milligrams C per milligram N; phase 2, 24.7 milligrams C per milligram N; phase 3, 91.9 milligrams C per milligram N; and phase 4, 47.7 milligrams C per milligram N.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins C. A., Pate J. S., Peoples M. B., Joy K. W. Amino Acid transport and metabolism in relation to the nitrogen economy of a legume leaf. Plant Physiol. 1983 Apr;71(4):841–848. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambley J., Grant D. B. Apparent heterogeneity of serum chorionic somatomammotrophin on gel filtration. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 May;70(1):43–47. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzell D. B., Pate J. S., Atkins C. A., Canvin D. T. Partitioning of carbon and nitrogen and the nutrition of root and shoot apex in a nodulated legume. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):30–36. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzell D. B., Rainbird R. M., Atkins C. A., Pate J. S. Economy of Photosynthate Use in Nitrogen-fixing Legume Nodules: Observations on Two Contrasting Symbioses. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):888–891. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. S., Atkins C. A., Hamel K., McNeil D. L., Layzell D. B. Transport of organic solutes in Phloem and xylem of a nodulated legume. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jun;63(6):1082–1088. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.6.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. S., Layzell D. B., McNeil D. L. Modeling the transport and utilization of carbon and nitrogen in a nodulated legume. Plant Physiol. 1979 Apr;63(4):730–737. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.4.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. S., Sharkey P. J., Atkins C. A. Nutrition of a developing legume fruit: functional economy in terms of carbon, nitrogen, water. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):506–510. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


