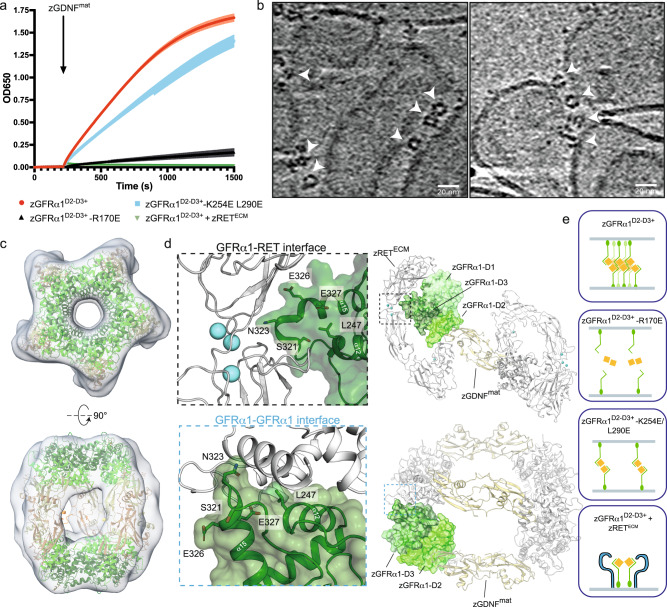
Fig. 3. Reconstitution of zGDNF-dependent trans-adhesion on liposomes is sensitive to pentameric interface mutation and addition of zRET extracellular module.
a Liposome adhesion assay using extruded liposomes coated with His-tagged zGFRα1 constructs as indicated. Liposome clustering was monitored by taking time-course measurements of absorbance at 650 nm (OD650). Arrow shows timepoint at which soluble zGDNFmat was added. Error bars represent standard deviation from three technical repeats. b 2D tomographic slices from reconstructed tomograms of zGDNFmat-zGFRα1D2-D3+-mediated liposome aggregates. Images show close-up views of bridging protein density between two liposome membranes (indicated with white arrow heads). Scale bar: 20 nm. c Subtomogram map of the zGDNFmat-zGFRα1D2-D3+ adhesion complex bridging adhered liposomes with the decameric complex crystal structure fitted into the map using ChimeraX77 ‘fit-in-map’ tool. Orthongonal views are shown. d Structural overlap between the high affinity GFRα1–RET interface and the GFRα1 pentameric interface. Top right, view of zGDNF-zGFRα1-zRETECM complex (PDB: 7AML) projecting down the two-fold molecular dyad. One zGFRα1 protomer is represented as a surface rendering coloured according to domain, zGFRα1-D1 light green, zGFRα1-D2 green and zGFRα1-D3 dark green. Top left, close up view of zRETECM and zGFRα1 interaction at a calcium-junction-D3 domain interface. Selected interacting residues shown as sticks and calcium atoms shown as blue spheres. Bottom right, view of the pentameric interface from the decameric zGDNFmat-zGFRα1D2-D3+ structure highlighting a single zGFRα1 protomer by surface rendering. Bottom left, close-up view of the pentameric interface highlighting the same interacting residues as shown for RET interaction. e Schematic representation of the LiCAM capacity of GFRα1 under defined conditions. (i) zGFRα1D2-D3+ acts as a strong adhesion molecule upon zGDNFmat addition through the ability to form homophilic interactions in cis. (ii) R170E mutation in zGFRα1D2-D3+ targets the ability of zGFRα1 to form interactions in trans and thereby abolishes the adhesive capacity of zGFRα1. (iii) Mutations targeting the cis pentamer interface, K254E L290E, lead to reduced adhesion function by zGFRα1 in the presence of zGDNFmat. (iv) In the presence of zRETECM, zGFRα1D2-D3+ preferentially forms a ternary complex in cis upon zGDNFmat addition.