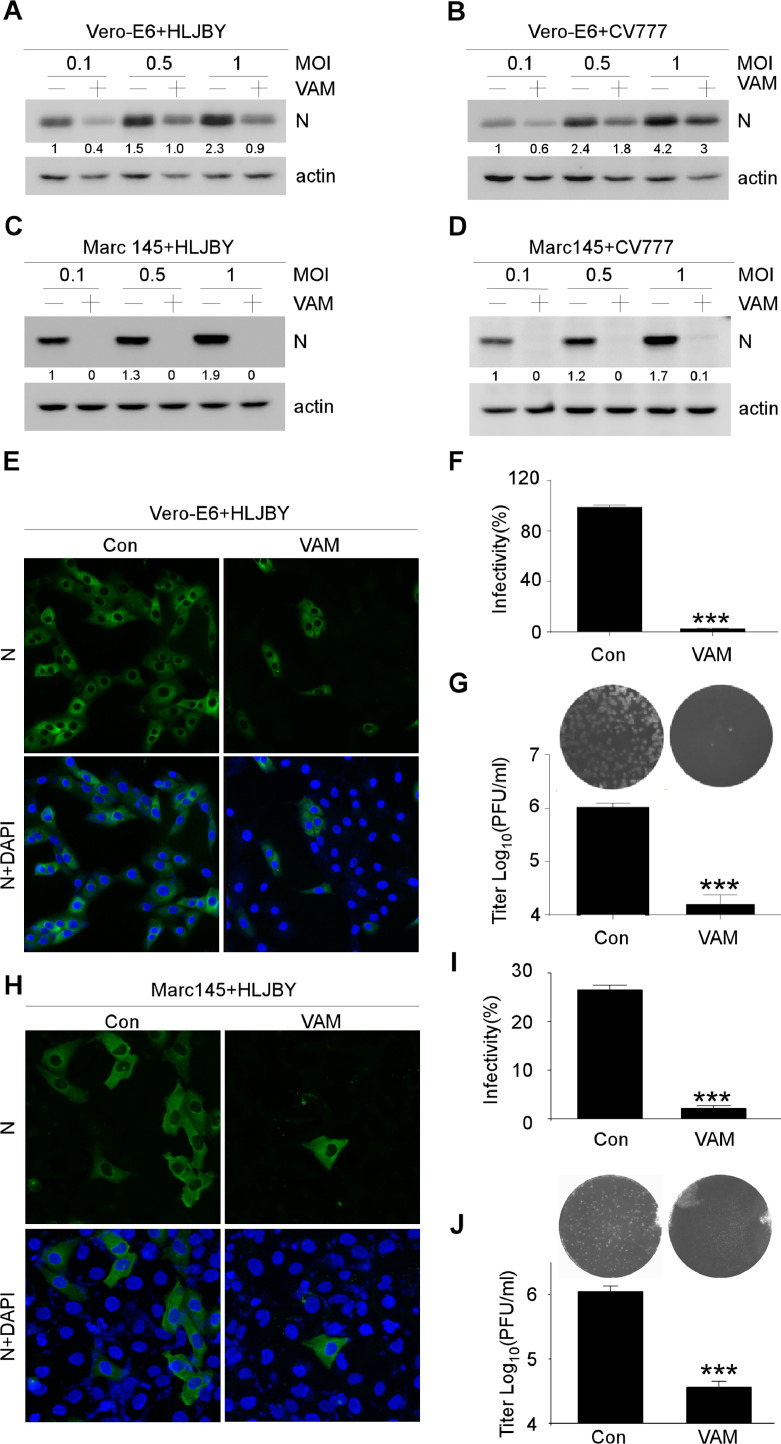
Fig. 2.
Antiviral activities of VAM on PEDV. (A-D) Vero-E6 or MARC-145 cells were pretreated with 10 μM VAM for 2 h and infected with 0.1, 0.5, or 1 MOI HLJBY or CV777. After 12 hpi, the cells were harvested and immunoblotting assay was performed to determine PEDV-N and actin protein levels. (E) Vero-E6 cells were pretreated with 10 μM VAM 2 h and infected with 1 MOI HLJBY for 12 h, and then fixed and stained with the rabbit-anti-PEDV-N antibody. The nuclei were stained with DAPI. (F) HLJBY positive cells were calculated in every 200 cells randomly. (G) Vero-E6 cells were pretreated with 10 μM VAM for 2 h, and infected with 1 MOI HLJBY for 12 h. After three freeze–thaw cycles, the viral titer was determined using plaque assay on Vero-E6 cells. (H) MARC-145 cells were pretreated with 10 μM VAM for 2 h and infected with 1 MOI HLJBY for 12 h, and then fixed and stained with the rabbit-anti-PEDV-N antibody. The nuclei were stained with DAPI. (I) HLJBY positive cells were calculated in every 200 cells randomly. (J) MARC-145 cells were pretreated with 10 μM VAM for 2 h, and infected with 1 MOI HLJBY for 12 h. After three freeze–thaw cycles, the viral titer was determined using plaque assay on Vero-E6 cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. The results were analyzed using the Student's t test: *, P < 0.05; ⁎⁎, P < 0.01; ⁎⁎⁎, P < 0.001. The levels of PEDV-N were normalized to the level of actin.