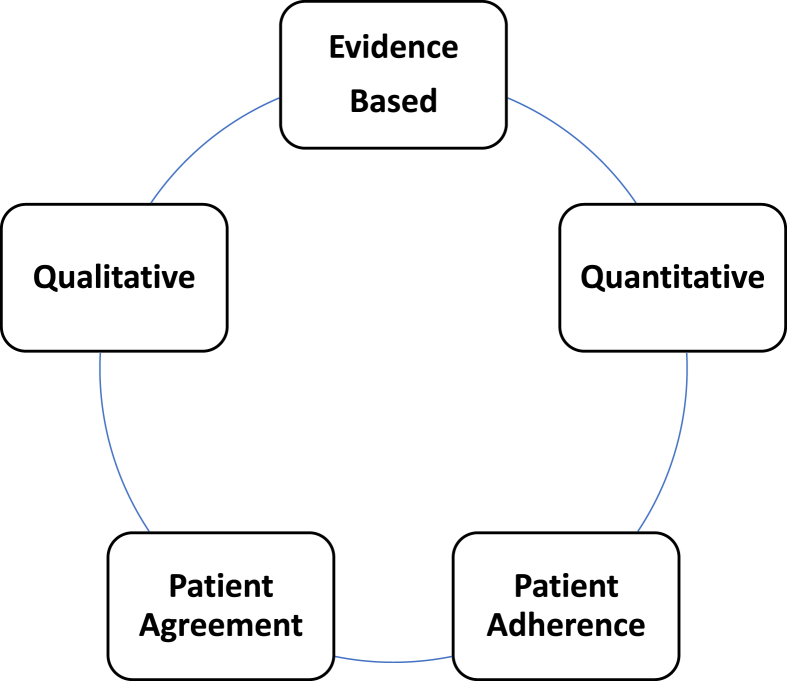
Fig. 1.
Nutrition Factors Associated with Improved Health Outcomes. Regarding medical nutrition therapy for obesity, the most effective approaches are evidence-based, consider both qualitative and qualitative aspects of dietary intake, and promote patient agreement and adherence. While possibly counterintuitive, randomized clinical trials do not necessarily support improved weight reduction when diets are based upon patient food preferences. In fact, meta-analyses suggest that patient choices in weight reduction strategies have no significant effect on duration or attrition, with greater weight reduction often occurring in the control groups. However, the effectiveness of any therapeutic intervention is likely enhanced when patients are engaged and agree to treatment plans [[6], [7], [8]].