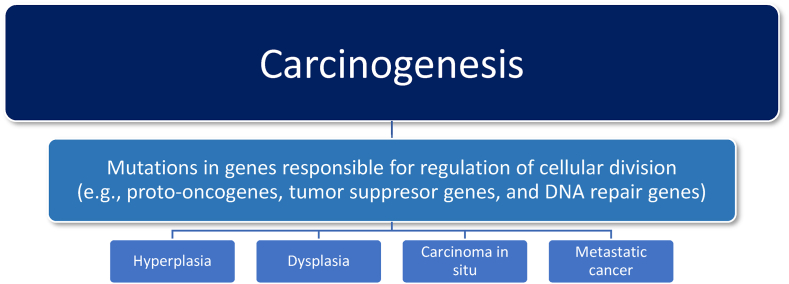
Fig. 2.
General mechanisms of carcinogenesis. Causes of cancer include genetic/epigenetic abnormalities, and/or environmental factors such as ultraviolet radiation, chemicals/toxins, viruses, and cigarette smoking. Obesity is also a facilitator of cancer. Disruption of orderly control of cell division (e.g., increased rate of cell division and/or impaired cell cycle arrest) can result in tissue hyperplasia (i.e., abnormal increase in cell number within a tissue or organ), dysplasia (i.e., abnormal cells within a tissue or organ), carcinoma in situ (i.e., malignant cells limited to the tissue origin), or metastasis (i.e., malignant growths at a distance from the primary tissue origin of the cancer).