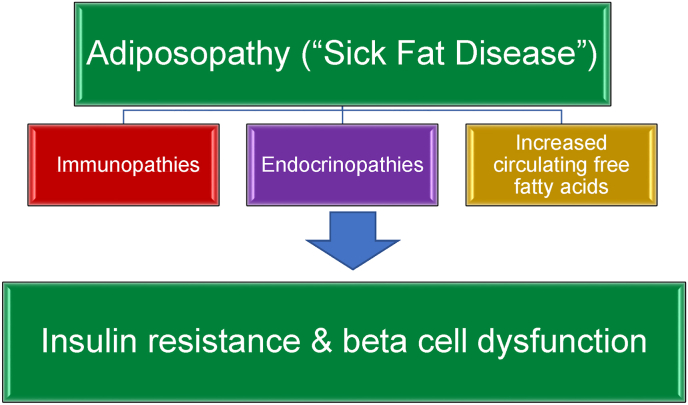
Fig. 1.
How does obesity (adiposopathy) contribute to type 2 diabetes mellitus? In addition to biomechanical abnormalities leading to “fat mass disease” [2] obesity may cause adiposopathy, or “sick fat disease [34].” Adipose tissue immunopathies, endocrinopathies, and increased circulating free fatty acids may lead to insulin resistance and beta cell dysfunction [[5], [6], [7], [8],32,33]. The degree by which the adiposopathic consequences of obesity promotes hyperglycemia depends on the crosstalk, interactions, and biometabolic responses of other body organs such as liver, muscle, pancreas, kidney and brain.