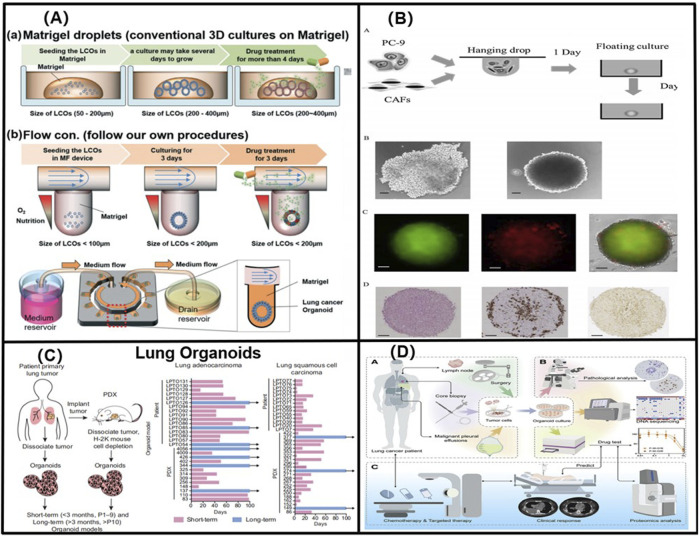
FIGURE 4.
(A) 3D lung cancer organoids in a size-controllable manner and demonstrates for the production of lung cancer organoids from patients with small-cell lung cancer. Adapted from Jung et al. (2019). Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry. (B) Using genetic engineering techniques to obtain LCOs with specific Kras-, Trp53-deficient, and Eml53-Alk mutations, which significantly accelerated the study of the lung cancer genetic mechanisms. Adapted from Nakamura et al. (2019). Copyright 2019, Elsevier B.V. (C) By constructing long-term (greater than 3 months, more than 10 generations), and short-term (less than 3 months, less than 10 generations) NSCLC organoid models, Shi found that cancer organoids with breast cancer 2 gene, EGFR, and EGFR- and EGFR-mutation/MSC-epithelial-transformation (MET)-amplified mutations responded favourably to lapatinib, erlotinib, and crizotinib, respectively. Adapted from Shi et al. (2020). Copyright 2020, American Association for Cancer Research. (D) A LCO-based drug susceptibility test (LCO-DST) of osimertinib, paclitaxel, pemetrexed, carboplatin, etoposide, and cisplatin. Adapted from Wang et al. (2023). Copyright 2023, Cell Press.