Figure 1.
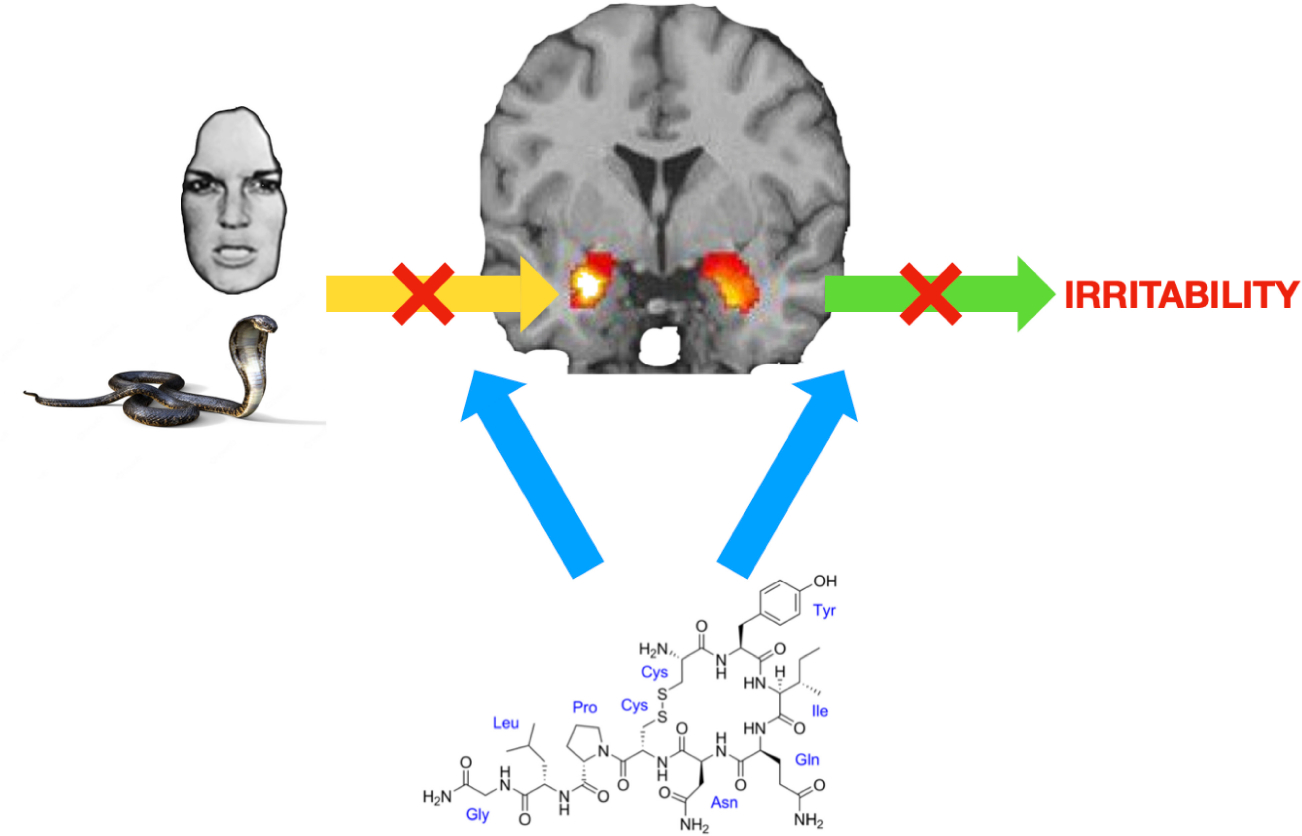
The potential modulatory neural impact of the neuropeptide hormone oxytocin as intranasal administration on the core mechanism of irritability. Oxytocin is known to reduce activation of the acute threat response system (in this figure, amygdala) to emotional stimuli (→). The most established neurobiological mechanism of irritability is increased activation of the amygdala in the acute threat response system to emotional stimuli (→), resulting in irritability (→).
