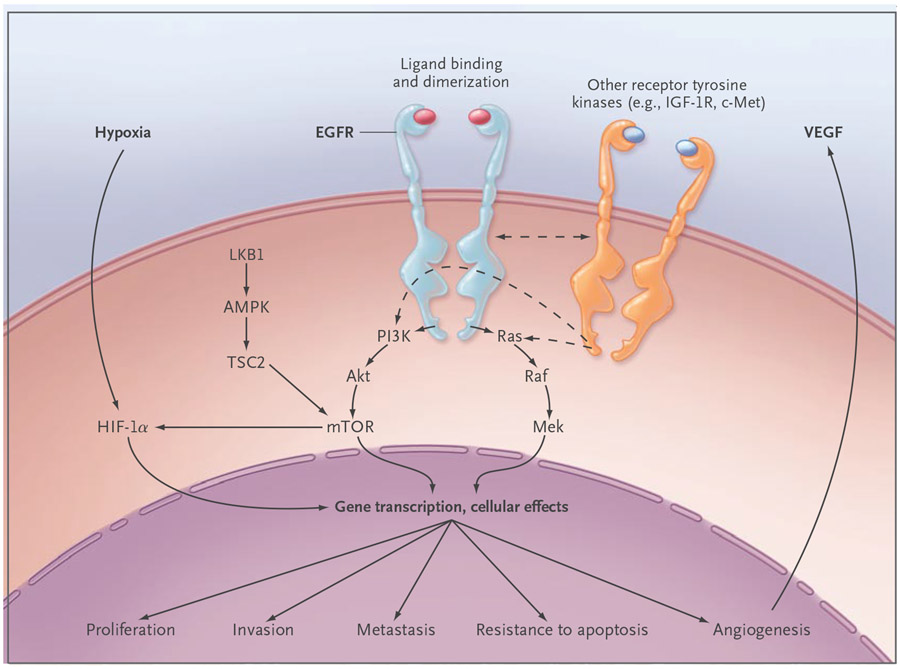
Figure 2. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Cell-Signaling Pathways.
EGFR activates several major downstream signaling pathways, including Ras–Raf–Mek and the pathway consisting of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt, and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), which in turn may have an effect on proliferation, survival, invasiveness, metastatic spread, and tumor angiogenesis through pathways that are either dependent on or independent of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF). These pathways also may be modulated by other receptor tyrosine kinases, such as insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) and cMET, and by the LKB1–amp-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which is involved in energy sensing and cellular stress. Most of these functions depend on signaling through the kinase domain. However, kinase-independent functions, such as maintaining glucose transport, have been reported.46 TSC2 denotes tuberous sclerosis complex 2, and VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor.