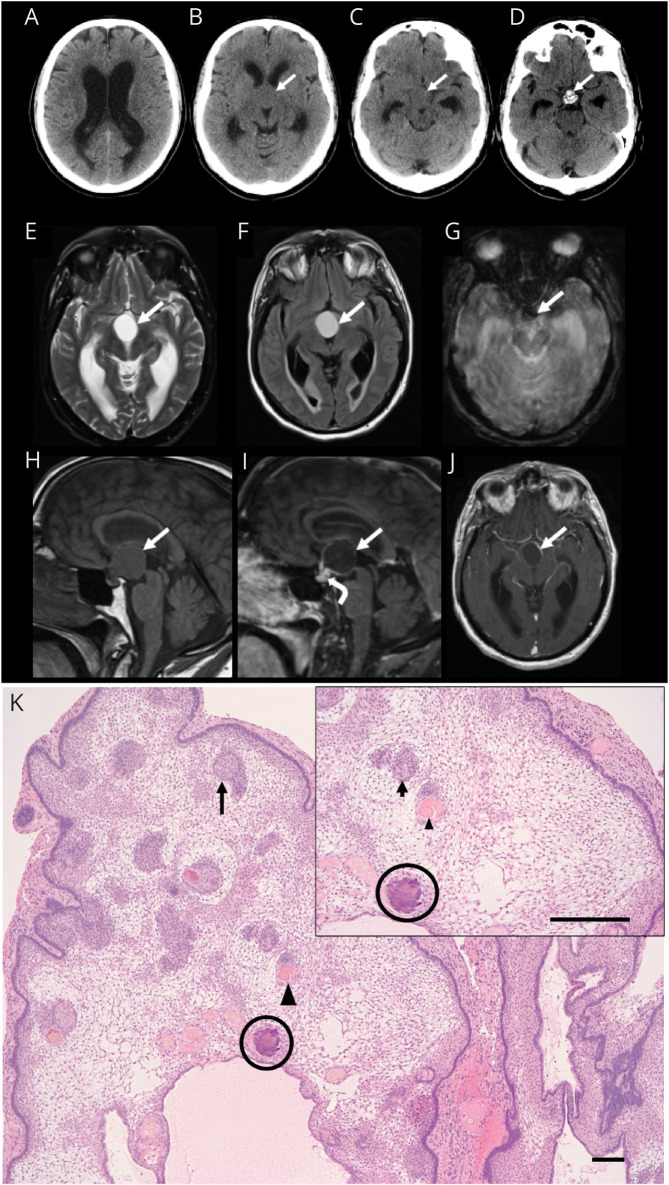
Figure 1. Neuroimaging and Histopathologic Findings of Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma.
Axial CT images demonstrating hydrocephalus with lateral ventricle dilatation (A) secondary to a suprasellar mass (arrow, B and C) with intrinsic calcification at its base anterior to the dorsum sella (arrow, D). MRI brain axial T2-weighted (E), fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (F), gradient-echo (G), and sagittal T1-weighted (H) images demonstrate a proteinaceous cyst in the suprasellar cistern with rim enhancement on sagittal (I) and axial (J) postcontrast T1-weighted images (solid arrows) and solid enhancement at the base of the lesion (curved arrow, I). Susceptibility artifact on the axial gradient-echo image (arrow, G) corresponds to the calcification at the base of the lesion. Paraffin-embedded, hematoxylin and eosin–stained section (K) reveals a multilobulated mass that is composed of palisading epithelium surrounding a loose stellate reticulum. Whorls of squamous epithelium (arrow), nodules of anucleate squames (arrowhead), and calcifications (circle) are present within the reticulum (scale bar 10 μm).