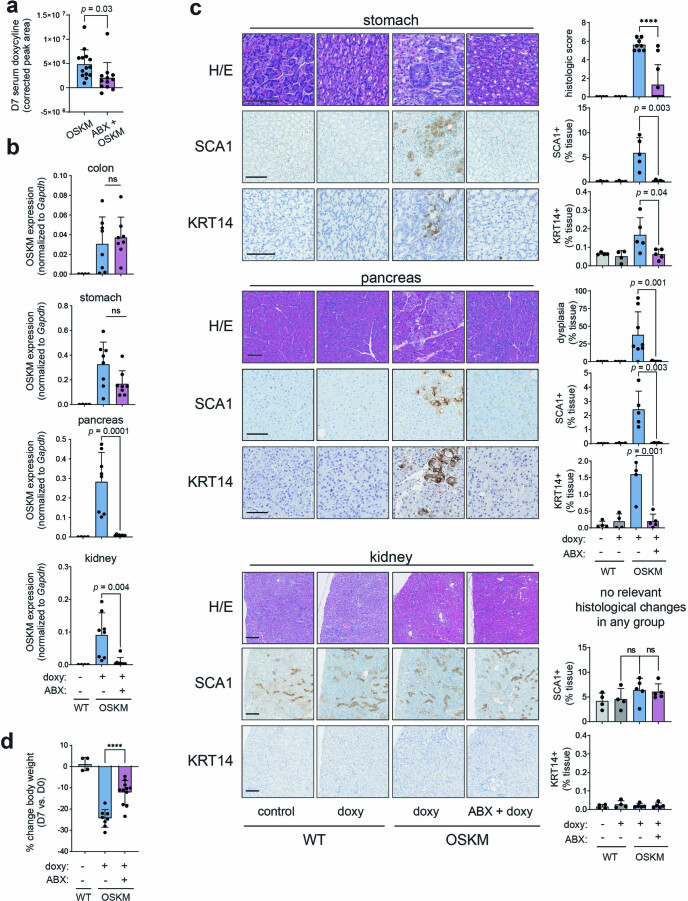
Extended Data Fig. 1. Broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment inhibits in vivo reprogramming.
(a-d) Mice were treated with doxycycline (doxy) and antibiotics (ABX) as described in Fig. 1a. (a) Serum was harvested from OSKM mice after 7 days of doxycycline treatment (OSKM n = 14; 5 M 9 F), or after ABX + doxycycline treatment (ABX + OSKM n = 12; 3 M 9 F) and doxycycline levels were analyzed by mass spectrometry. The total area of the doxycycline peak corrected for background levels for each mouse is shown. (b-d) Representative subsets of mice from Fig. 1b n = 4 mice (WT; 3 M 1 F), n = 8 (OSKM + doxy; 4 M 4 F), n = 11 (OSKM + doxy + ABX 4 M 7 F) were used for all analyses (b) Tissues were harvested on day 7 post doxycycline initiation and the expression of the OSKM transgene was assessed by RT-qPCR. (c) Representative histology images of the indicated treatments and markers are shown (left) and quantified (right). Histologic score for stomach dysplasia and inflammation was assigned by a blinded pathologist. No relevant morphologic changes were observed in the kidney cortex and medulla in any of the mice. (d) Body weights of mice from the indicated treatment groups, expressed as a percent change on day 7 post-doxycycline as compared to pre-doxycycline (day 0). Scale bars are 100 µm. Graphs represent average ± SD; ****p < 0.0001 by two-tailed Student’s t-test.