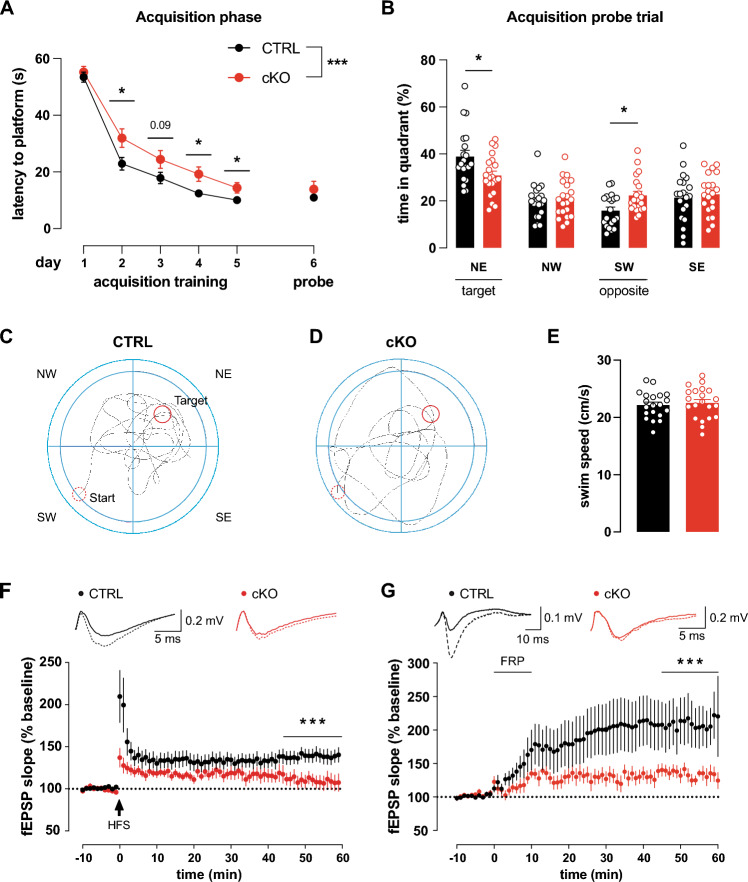
Fig. 2.
Impaired MWM performance and hippocampal LTP in cKO. A–C Compared to CTRL (N = 20), cKO (N = 21) exhibit delayed learning and reduced memory in the MWM task. A Mean latencies to reach the hidden platform or original platform position over 5 training days (4 training sessions per day). Latency was similar on day 1 but decreased quicker in CTRL than cKO during the following trainings days. Since the hidden platform was removed, latency during probe trial on day 6 was measured for reaching the former platform position. The latency of the probe is offset, as it is not part of the acquisition phase. B CTRL but not cKO showed significant target quadrant (NE) preference during probe trial and also significantly avoided the opposing quadrant (SW). C Representative paths traveled by the CTRL and D cKO during acquisition probe trial. Start and finish indicated by dashed and solid red circle, respectively. E Swim speed of CTRL (N = 20) and cKO (N = 21) during acquisition probe trial were comparable. F Schaffer-collateral fEPSP initial slopes recorded from forebrain slices. 100 Hz 1 s high frequency stimulation (HFS) induced significantly more LTP in CTRL (n = 7 slices from N = 4 animals) than cKO (n = 8 slices from N = 4 animals). Top: Representative traces before (solid) and after (dashed) LTP induction. G Schaffer-collateral fEPSP initial slopes recorded from forebrain slices. 10 min perfusion of 20 µM forskolin, 50 µM picrotoxin and 0.1 µM rolipram (FRP) induced significantly more cLTP in CTRL (n = 10 slices from N = 4 animals) than cKO (n = 10 slices from N = 5 animals). Top: Representative traces before (solid) and after (dashed) LTP induction. Statistics: Two-way ANOVA (F, G) with Sidak's multiple comparison test (A, B), unpaired Student's t-test (E). All bar diagrams presented as means ± SEM. See also Fig. S2 and Table S2