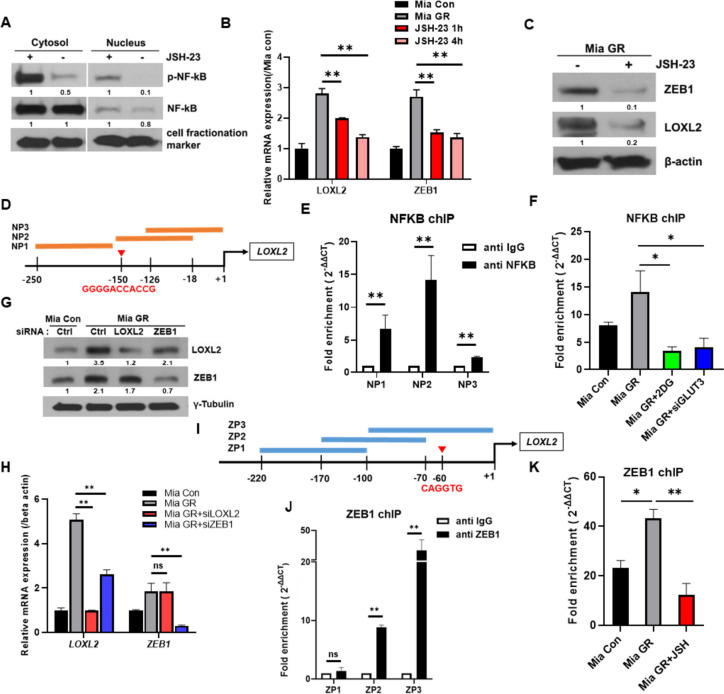
Fig. 4.
NF-kB directly regulates LOXL2 expression or indirectly through ZEB1. A Immunoblotting for phospho NF-κB and NF-κB using nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions prepared from Mia GR cells after treatment with JSH-23 for 4 h. Relative mRNA expression (B), and protein expression (C), of LOXL2 and ZEB1 in Mia Con, Mia GR (no treatment, JSH-23 1 h or 4 h treatment) cells. D Scheme for the expected NF-kB binding site on the LOXL2 gene promoter. E ChIP fold enrichment of LOXL2 DNA fragments (NP1, NP2, NP3) by chIP-qPCR. F Changes in chIP fold enrichment with NF-kB in the NP2 region on the LOXL2 gene promoter in Mia Con and Mia GR cells (no treatment, 2DG treatment, and siGLUT3 transfection) (G), Mia GR cell transfected with LOXL2 and ZEB1 siRNA. Knockdown efficiencies were evaluated by immunoblotting using LOXL2 and ZEB1 antibodies. H Relative gene expression of LOXL2 and ZEB1 confirmed by qPCR in Mia GR transfected with siRNA. I Scheme for the expected ZEB1 binding site on the LOXL2 gene promoter. J ChIP fold enrichment of LOXL2 DNA fragments (ZP1, ZP2, ZP3) by chIP-qPCR. K Changes in chIP fold enrichment with NF-kB in the ZP3 region on the LOXL2 gene promoter in Mia Con and Mia GR cells (no treatment, JSH-23 4 h treatment)