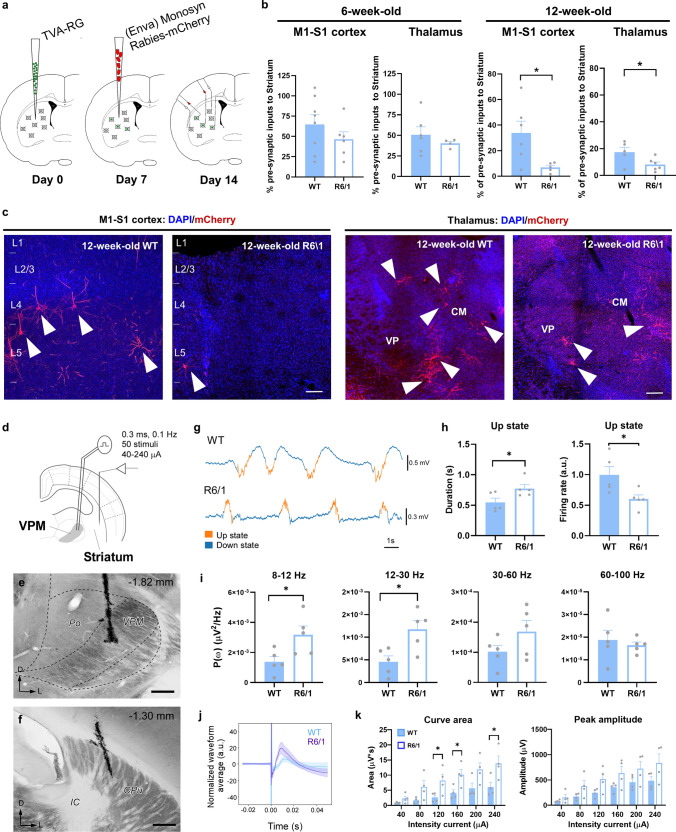
Fig. 1.
Striatal synaptic inputs assessment in the R6/1 mouse model. a Schematic representation of the experimental design for the Rabies-virus approach. b Histograms showing quantitative analysis of cortical and thalamic pre-synaptic inputs in 6- (left panels) or 12-week-old R6/1 (right panels) and WT mice. c Representative micrographs of pre-synaptic inputs in 12-week-old R6/1 and WT mice M1-S1 cortex (left panels) and thalamus (right panels). d Schematic representation of the experimental setup for in vivo electrophysiological recordings in a representative coronal section in 12-week-old WT and R6/1 mice. e, f Representative image of a mouse brain section stained for cytochrome oxidase showing the location of the bipolar electrode tip in the VPM (e) and the tungsten electrode in the striatum f. Scale bars: 250 µm. The anteroposterior level respect to bregma is indicated (upper right corner). g Spontaneous local field potentials (LFP) were recorded during slow oscillation activity in deeply anesthetized mice. Representative traces are shown. Up and down events are in orange and blue respectively. h Quantification of the Up states mean duration (in seconds; left panel) and the mean firing rate (arbitrary units; right panel) during the Up states. i Averaged power spectral density (PSD) over the z-scored normalized LFP of oscillatory activity at different frequency bands (alpha, 8–12 Hz; beta, 12–30 Hz; low-gamma, 30–60 Hz; high-gamma, 60–100 Hz). j Representative normalized evoked responses in the striatum after thalamic stimulation at 80 µA in WT (blue) and R6/1 (purple) mice. Solid lines, averaged waveforms; shaded areas, standard deviation. k The area under the curve (left panel) and the peak amplitude (right panel) were quantified for each current intensity tested, data in the range of 40–240 µA intensity currents are shown. Data are means ± SEM. * p < 0.05 compared to WT controls. Two-tailed unpaired t-test was employed in b, f, i, and k. n = 4–8 per genotype. Po posterior thalamic nucleus, CPu caudate putamen/striatum, IC internal capsule, CM Centro-medial nucleus, VPM ventral posteromedial nucleus