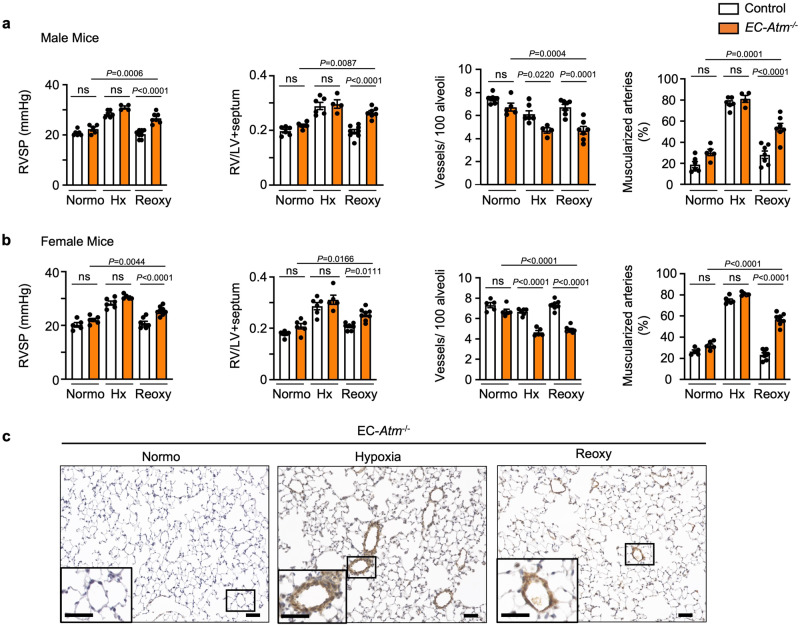
Fig. 3. EC specific Atm deletion in mice induces persistent PAH after reoxygenation.
EC-Atm-/- and control mice were subjected to (i) 7 weeks of room air (Normo), or (ii) 3 weeks of hypoxia (10% O2, Hx) only, or (iii) 3 weeks of hypoxia (10% O2), followed by 4 weeks of reoxygenation in normoxia (Reoxy). Right ventricular (RV) systolic pressure (RVSP), RV hypertrophy (weight of RV/left ventricle and septum, RV/LV + S), number of vessels per 100 alveoli at alveolar wall and duct level, and the percentage of fully or partially muscularized pulmonary arteries in (a) male mice (Control: Normo n = 6, Hx n = 6, Reoxy n = 8; EC-Atm-/-: Normo n = 5, Hx n = 4, Reoxy n = 7) and (b) female mice (Control: Normo n = 5, Hx n = 6, Reoxy n = 7; EC-Atm-/-: Normo n = 6, Hx n = 5, Reoxy n = 8). Each data point represents a mouse. Bars represent mean ± S.E.M. P values determined by 2-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak posthoc test. ns, not significant. c Representative images of αSMA staining of lung section in EC-Atm-/- mice. Scale bars, 20 μm. Inserts in the lower left corners show a magnified image of vessels delineated by the black lines (Scale bars, 20 μm). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.